Dec 19, 2025
Transparency in AI builds trust by making systems easier to understand and ensuring users feel in control. When AI tools explain how they work, handle data responsibly, and acknowledge limitations, users are more likely to rely on them. For example, platforms like NanoGPT show which AI model is used, store data locally, and avoid using customer data for training - addressing privacy concerns head-on.
Key takeaways:
In industries like healthcare and finance, transparency improves decision-making and user confidence. By balancing clarity with privacy, AI tools can meet user expectations without overwhelming them.
Trust Levels in AI Systems: Transparent vs Opaque AI Compared to Human Experts
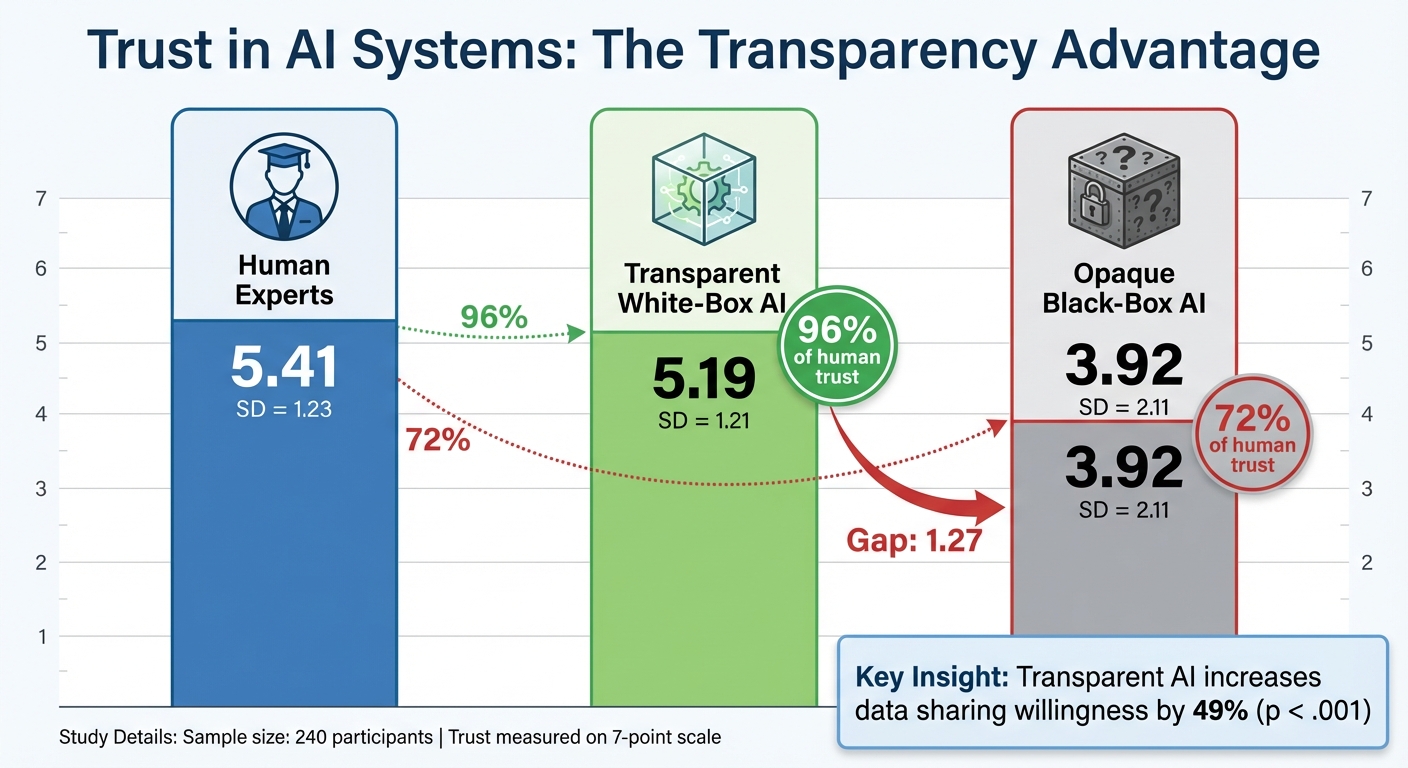
A fascinating experiment with 240 participants compared trust levels in three scenarios: human experts (M = 5.41, SD = 1.23), transparent white-box AI (M = 5.19, SD = 1.21), and opaque black-box AI (M = 3.92, SD = 2.11). The results showed that people were more inclined to trust transparent systems than opaque ones, even though they still slightly favored human experts.
Transparency also influenced user behavior. In the transparent AI condition, participants were more willing to share their data (B = 0.49, p < .001). This suggests that when users can see how an AI operates, they feel more comfortable engaging with it - especially those who already have a baseline trust in AI technology.
Other experiments highlighted how transparent features like error reporting and confidence scores impact trust. These tools help users develop what researchers call "calibrated trust" - trusting the AI when it’s likely correct and being cautious when it’s not. This balance leads to more consistent use of AI systems and fewer mistakes over time.
These findings play out in real-world scenarios across industries. For example, HSBC’s AI-driven customer support system offers explanations for its actions, such as why a transaction was flagged as suspicious. This transparency has led to happier customers, less frustration, and a greater sense of control.
In healthcare, the benefits of transparency are even more striking. Hospitals using decision-support tools with clear error reporting and explanations have found that clinicians continue to trust and use the systems - even after initial mistakes. In contrast, opaque systems often lose user trust after a single error. Transparent systems that provide evidence summaries and confidence levels also see better acceptance, especially in high-stakes environments like emergency rooms and diagnostics. When doctors understand the reasoning behind AI recommendations, they are more likely to use the tools thoughtfully - neither blindly following them nor dismissing them outright.
Incorporating transparency into text generation tools isn't just a nice-to-have - it’s essential for building trust with users. By opening up about how these tools work, platforms can demystify their processes and make users feel more confident in the results. For example, when a platform explains its reasoning or shows which AI model generated a response, it mirrors the benefits of clear decision-making explanations that research has consistently highlighted.
Take NanoGPT as an example. Its Auto Model feature doesn’t just pick an AI model for you - it shows exactly which one is being used, whether it’s ChatGPT, Gemini, or another engine. This avoids the "black box" problem, where users are left guessing about the source of their content. NanoGPT goes a step further with side-by-side comparisons, allowing users to query multiple models simultaneously. This way, professionals can compare responses for accuracy and relevance without juggling between platforms or subscriptions, making it easier to validate information.
Privacy is another cornerstone of transparency. NanoGPT addresses this by storing conversations locally on users' devices and ensuring that model providers don’t train on customer data. This approach directly tackles privacy concerns, which often deter users from sharing sensitive information with AI tools. Research backs this up - when users understand how their data is handled, they’re more likely to engage with the technology (B = 0.49, p < .001 in transparent conditions).
The same principles of transparency also apply to image generation tools, which come with their own unique challenges.
Image generation tools face a different set of transparency hurdles, especially when it comes to explaining how training data is sourced and how prompts are transformed into visuals. Platforms like DALL-E and Stable Diffusion address this by openly sharing their training datasets, such as LAION-5B. This allows users - whether they’re designers, marketers, or other professionals - to understand potential biases in the models and adjust their prompts accordingly for better results.
Another way these tools enhance transparency is through confidence scores and generation metadata. Instead of just delivering an image, a transparent system might indicate how confident it is in the output or explain the steps it took during the generation process. NanoGPT brings this level of openness to image generation, too. It provides access to multiple models, like DALL-E and Stable Diffusion, through a pay-as-you-go platform. And just like its text generation tools, NanoGPT ensures that all data stays local, addressing privacy concerns across both text and image workflows.
Striking the right balance in transparency is no easy feat. Share too much detail, and you risk overwhelming users with technical jargon, which can erode confidence when errors arise. On the other hand, offering too little information leaves users skeptical, often perceiving the AI as an impenetrable "black box".
Different users have different needs. Experts often seek in-depth technical details, while everyday users benefit more from concise, outcome-oriented explanations. For example, research indicates that numeric transparency - like stating an "85% accuracy" - can confuse non-technical users who may not fully grasp what that figure represents.
A layered approach can help bridge this gap. Providers might start with simple, plain-language explanations for general users, while offering more detailed technical documentation for those who want it - such as experts or regulators. Instead of inundating everyone with algorithmic specifics, the key is to explain decision-making in clear terms and provide an option to dive deeper for those interested. This method not only simplifies AI for the average user but also ensures that those seeking technical insight can access it without overwhelming others. Balancing clarity and detail naturally leads to another critical challenge: addressing privacy concerns tied to transparency.
Balancing transparency with privacy is a delicate act. Offering insights into how AI systems make decisions often involves revealing processing details, which could inadvertently expose sensitive data. Studies have shown that, while users value transparency, they also prioritize the protection of their personal information. Users want to understand how AI functions but without sacrificing their privacy in the process.
Cloud-based systems add another layer of complexity, as users must trust that their data stored on company servers remains secure. To tackle this, NanoGPT has taken a unique approach by storing conversations locally on users' devices. This "leave no trace" method ensures that transparency about AI processes - like which model is being used - doesn’t compromise privacy. Additionally, NanoGPT enforces strict guidelines prohibiting providers from using customer data for training models, addressing concerns that sensitive information could inadvertently feed into future AI training sets. This approach demonstrates how transparency and privacy can coexist without one undermining the other.
Transparency is the backbone of trust in AI systems. Studies have shown that when AI tools clearly explain their decisions and openly acknowledge their limitations, users feel more confident and satisfied. A great example is HSBC's AI chatbots, which boosted customer satisfaction by explaining why specific transactions were flagged. This gave users both clarity and a sense of control.
Pairing clear explanations with confidence metrics empowers users to make informed choices. Instead of blindly accepting or rejecting AI outputs, users are more likely to engage with systems they understand. Research highlights that transparent AI systems significantly increase users' willingness to share data (B=0.49, p<.001).
Platforms like NanoGPT illustrate how transparency and ethical practices can work together seamlessly. By storing user conversations locally and adopting a pay-as-you-go model without subscriptions, NanoGPT addresses privacy concerns while remaining accessible. Additionally, their strict policies against using customer data for model training show that transparency and privacy don't have to be at odds.
The next phase of AI transparency isn't just about showing more information - it's about delivering smarter, user-focused solutions. Researchers are working on systems that adapt transparency levels to the needs of different users. For example, casual users might receive simple explanations, while technical experts and regulators could access detailed documentation. This approach ensures that everyone gets the information they need without feeling overwhelmed.
Regulations will also shape the future of transparency. Laws like the EU’s Digital Services Act are pushing AI developers to adopt consistent disclosure practices, offer clearer explanations of algorithms, and improve accountability. Looking ahead, we can expect innovations like advanced confidence indicators, tools for tracking performance over time, and hybrid AI systems designed to help users calibrate their trust in a more nuanced way. These advancements aim to provide users with the right information at the right time, making AI interactions more confident and informed.
Transparency in AI plays a crucial role in building user trust by shedding light on how decisions are made, holding systems accountable, and addressing concerns head-on. Take healthcare, for example - when AI systems are transparent, patients are more likely to trust their diagnoses. In finance, transparency reassures users by showing compliance with regulations and promoting fairness. In customer service, it makes interactions clearer and more satisfying, while in legal settings, it reinforces the sense of fairness and impartiality.
NanoGPT takes transparency and privacy seriously. By storing data locally on the user’s device and steering clear of using personal data for model training, it ensures users retain full control over their information. This approach strengthens trust and underscores a commitment to user privacy.
Transparency in AI comes with its own set of challenges, especially when it comes to privacy. Revealing how user data is processed or stored can foster trust, but it also risks exposing sensitive details if not managed properly.
Take NanoGPT, for example. This platform emphasizes user privacy by keeping data stored locally on your device. Plus, it ensures that your conversations aren’t used for training AI models. Despite these protections, being more transparent still requires careful handling to prevent accidental data exposure or misuse.
AI systems can strike a balance between being transparent and not overwhelming users by offering clear, straightforward explanations. One way to do this is by presenting simple summaries first, while giving users the option to explore more detailed information if they want to dig deeper.
Another helpful feature is intelligent model selection, which ensures users get responses that are both relevant and easy to understand. This method not only simplifies communication but also helps build trust, all while keeping the experience smooth and user-friendly.