Nov 18, 2025
AI image generators, like Stable Diffusion and DALL-E, often reflect societal biases, such as stereotyping CEOs or judges as predominantly white males. To address this, tools for detecting bias in AI-generated images are essential. Five key tools - IBM AI Fairness 360, Fairlearn, Google What-If Tool, Aequitas, and TIBET - offer solutions to identify and reduce bias. Each has unique features, strengths, and limitations, making them suitable for different needs.
| Tool | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| IBM AI Fairness 360 | Broad ML pipeline integration, detailed metrics | Steep learning curve, technical expertise needed |
| Fairlearn | Detailed metrics, Python-friendly | Requires ML knowledge |
| Google What-If Tool | Intuitive, no-code interface | Limited offline use, Google-reliant |
| Aequitas | Audit-ready reports, compliance focus | No real-time detection |
| TIBET | Focused on text-to-image models, strong privacy | Performance depends on training data |
Selecting the right tool depends on your goals - whether you prioritize technical depth, ease of use, compliance, or privacy. With generative AI expected to produce 10% of all data by 2025, addressing bias is more important than ever.
IBM AI Fairness 360 is an open-source toolkit designed to help detect and reduce bias in machine learning systems. It addresses bias at every stage of the development process - whether it’s before, during, or after the model is trained. This makes it a valuable resource for organizations aiming to create fair and unbiased AI solutions.
IBM AI Fairness 360 identifies various types of bias, including demographic parity, equalized odds, and individual fairness. Its modular structure ensures it can be integrated into existing machine learning workflows without requiring a full system redesign. This flexibility makes it a practical choice for diverse applications, including AI-powered image generation systems.
The toolkit stands out for its clear documentation and active community support, making it easier to understand and implement. Since it’s open source, users can dig into the algorithms to see exactly how it detects and addresses bias. This transparency has made it a trusted tool in both academic research and enterprise environments.
Built in Python, IBM AI Fairness 360 works smoothly with widely-used machine learning frameworks like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch. Its compatibility extends to popular AI platforms such as NanoGPT and supports models like DALL‑E and Stable Diffusion. This ensures it can integrate effectively into various AI workflows, including those focused on image generation tasks.
For organizations navigating strict regulations, IBM AI Fairness 360 offers robust reporting features that align with U.S. compliance standards. These features help document bias detection and mitigation efforts for audits and enterprise reviews. However, implementing its advanced capabilities often requires expertise in Python and machine learning, making specialized knowledge essential for effective use.

Fairlearn is an open-source Python toolkit developed by Microsoft to help identify and reduce bias in machine learning models. While it's not specifically designed for image generation, it offers powerful tools for analyzing fairness in AI systems, including those that create visual content. The toolkit focuses on three main areas: group fairness, individual fairness, and counterfactual fairness.
Fairlearn stands out for its ability to provide detailed metrics and visual tools for detecting bias, making it a great choice for academic research and Python-based projects. It calculates fairness metrics like demographic parity and equalized odds, which are particularly useful for analyzing bias in image outputs.
For example, a study published in the European Heart Journal demonstrated how Fairlearn's metrics and visualizations effectively revealed gender bias in AI-generated professional images.
However, its performance largely depends on the user's technical expertise. Successfully integrating image generation models into Python and interpreting the results requires advanced skills. While it may not be the most beginner-friendly tool, it offers deep insights into model biases for those who can navigate its technical demands.
One of Fairlearn's key strengths is its commitment to transparency. The toolkit provides thorough explanations of the metrics it uses and includes visualizations to help users better understand the sources and extent of bias in their models. Its dashboards and plots clearly show how different demographic groups are impacted by model outputs, enabling developers to pinpoint specific problem areas.
This level of transparency is especially valuable for organizations that need to document and justify their efforts to address bias. It’s particularly useful in compliance-driven environments. Being open source, Fairlearn also allows users to examine its algorithms, which builds trust and offers the flexibility to customize it for specific needs.
For developers working with Python-based image generation models, Fairlearn integrates smoothly with tools like scikit-learn and Azure ML, making it easier to incorporate bias analysis into workflows. This compatibility extends to a wide variety of AI models, including those used for generating images. To use Fairlearn effectively with image generators, developers may need to convert image outputs into formats like feature vectors or labels that the toolkit can analyze.
Organizations utilizing platforms such as NanoGPT, which supports models like DALL‑E and Stable Diffusion, can leverage Fairlearn as a valuable layer for bias detection within their development pipelines.
Fairlearn helps organizations meet U.S. regulatory standards for algorithmic fairness by offering detailed documentation and reporting features. These tools allow users to generate reports on bias metrics and mitigation efforts, which can support compliance with guidelines like those from the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC).
That said, Fairlearn does not directly address data privacy. Users must handle privacy concerns separately to meet regulatory requirements. For teams with strict privacy needs, combining Fairlearn's bias detection capabilities with privacy-focused solutions that store data locally can create a more comprehensive approach to responsible AI development.
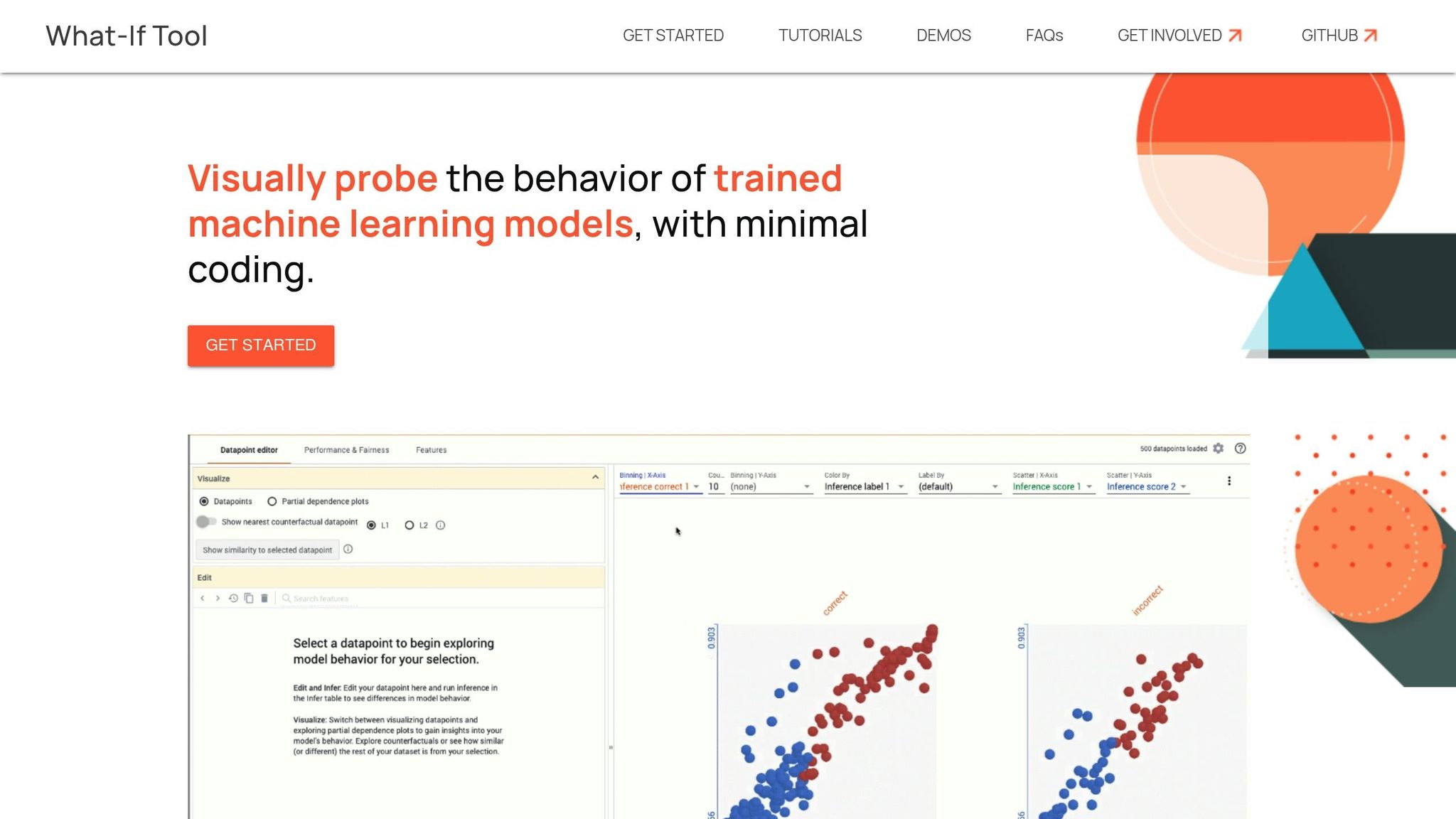
The Google What-If Tool is an interactive, open-source platform designed to help users explore machine learning models for potential bias and fairness concerns. What sets it apart is its focus on visual exploration and counterfactual analysis, making it easier to use, even for those without programming expertise. This tool is particularly useful for auditing AI image generators, as it allows users to test and visualize how changes in input features affect outcomes in real time.
A key feature is the ability to tweak input attributes - such as demographic details in text prompts - and instantly see how the model's predictions or outputs change. For AI image generation, this means developers can adjust variables like gender or ethnicity in prompts and observe how the generated visuals differ. This hands-on, visual approach simplifies bias detection and makes it faster to identify problematic patterns.
Built for real-time analysis, the What-If Tool handles large datasets efficiently. It works seamlessly with TensorFlow and provides immediate visual feedback when parameters are adjusted. For instance, by modifying demographic attributes in prompts, users can quickly spot biases, such as a tendency to depict doctors predominantly as male or certain ethnic groups being underrepresented. The tool also includes fairness metrics like scatter plots and confusion matrices to highlight disparities in model behavior. However, its deep integration with Google's ecosystem might pose limitations for users relying on non-Google workflows.
Transparency is one of the tool's standout features. It offers clear, visual explanations of how models behave and how bias metrics are calculated, making it accessible even to those without technical expertise. The tool supports intersectional analysis, allowing users to examine how combined factors - like race and gender - affect model outputs. This capability helps organizations pinpoint specific areas where bias may arise. Additionally, the visual nature of the tool makes it easier to communicate findings to non-technical stakeholders, aligning with efforts to create fair and trustworthy AI systems.
The What-If Tool is designed to integrate smoothly with TensorFlow models and is compatible with Jupyter notebooks and cloud platforms. This makes it a natural choice for teams already working within standard machine learning workflows. It's widely used in academic and research settings to teach and demonstrate fairness concepts. For those using NanoGPT, the tool can act as an additional layer for analysis, though some workflow adjustments or model conversions may be necessary for full compatibility. Its code-free interface further lowers the barrier for auditing AI image generators, making it accessible to a broader audience.
The tool's detailed bias and fairness reports can help organizations meet regulatory requirements under U.S. anti-discrimination laws. However, it does not include built-in privacy controls or direct support for specific regulatory frameworks. Teams must ensure their data handling practices comply with local legal standards. While the tool's comprehensive visual reports can aid in documenting compliance, organizations with strict privacy or regulatory needs may need additional tools to supplement it. Because it operates in the cloud, teams handling sensitive data might also need to implement extra privacy measures or combine the tool with locally managed, privacy-focused solutions.

Aequitas is an open-source toolkit designed to audit AI systems for bias, focusing on how different demographic factors intersect and influence algorithmic decisions. Unlike tools built for real-time monitoring, Aequitas is tailored for post-deployment audits, making it particularly useful for organizations that need to showcase fairness in their algorithms to regulators or stakeholders.
What sets Aequitas apart is its ability to analyze the combined effects of demographic attributes - like gender and race - on AI outcomes. For example, in AI-driven image generation workflows, it doesn’t just evaluate these factors individually but examines how they work together to impact decisions. The toolkit is accessible via a command-line interface and a Python-based web interface, catering more to research and compliance needs than enterprise-level production environments.
Aequitas is all about detailed, post-deployment bias analysis. It uses statistical methods to assess fairness across demographic groups, producing reports that evaluate both the equity of outcomes and the fairness of processes. For instance, consider an AI system that generates profile images and classifies candidates for job suitability. Aequitas can audit these classification outcomes to identify disparities in selection rates across different demographic groups. However, this requires structured data inputs - like CSV files - that include demographic information, predicted outcomes, and ground truth labels. Teams must preprocess and organize the data before using Aequitas, ensuring all relevant features are extracted and ready for analysis.
One of Aequitas’ strongest features is its clear and accessible reporting system. It generates detailed reports outlining the fairness metrics used, the demographic groups analyzed, and the specific results of the bias audit. These reports are designed to be easily understood by both technical teams and non-technical stakeholders, making them especially useful for organizations needing to comply with anti-discrimination laws or explain their algorithms to external auditors. Its intersectional analysis also uncovers complex bias patterns, such as how individuals belonging to multiple demographic groups may be uniquely affected. This transparency allows Aequitas to fit seamlessly into existing audit workflows, ensuring organizations can effectively communicate their findings.
Built in Python, Aequitas works with structured outputs from image generation systems, such as metadata or classification results. However, it does not process raw image data directly. This means teams need to pair it with other tools for image analysis or feature extraction to assess bias within the content itself. While this extra preprocessing step adds complexity, it also offers flexibility for organizations with specific analytical needs. For instance, teams using NanoGPT’s image generation models can integrate Aequitas as a bias auditing layer, provided they use appropriate preprocessing tools to prepare the data.
Aequitas is designed with regulatory compliance in mind, offering documentation and reporting features that align with U.S. fairness standards. Its focus on intersectional analysis and outcome equity supports organizations in meeting legal and ethical obligations, such as those outlined by the EEOC and similar frameworks. Its audit reports can serve as evidence of bias detection and mitigation efforts, which may be crucial during legal proceedings or regulatory reviews. However, teams must ensure their data handling practices meet privacy regulations, as Aequitas does not include built-in privacy controls beyond standard data security measures.
TIBET (Tool for Identifying Bias in Emerging Technologies) is a framework designed specifically to detect and measure biases in AI-generated images. While many fairness tools take a one-size-fits-all approach, TIBET focuses on text-to-image models - like Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, and DALL-E - and adapts its analysis based on the specific context of each prompt rather than relying on a fixed checklist.
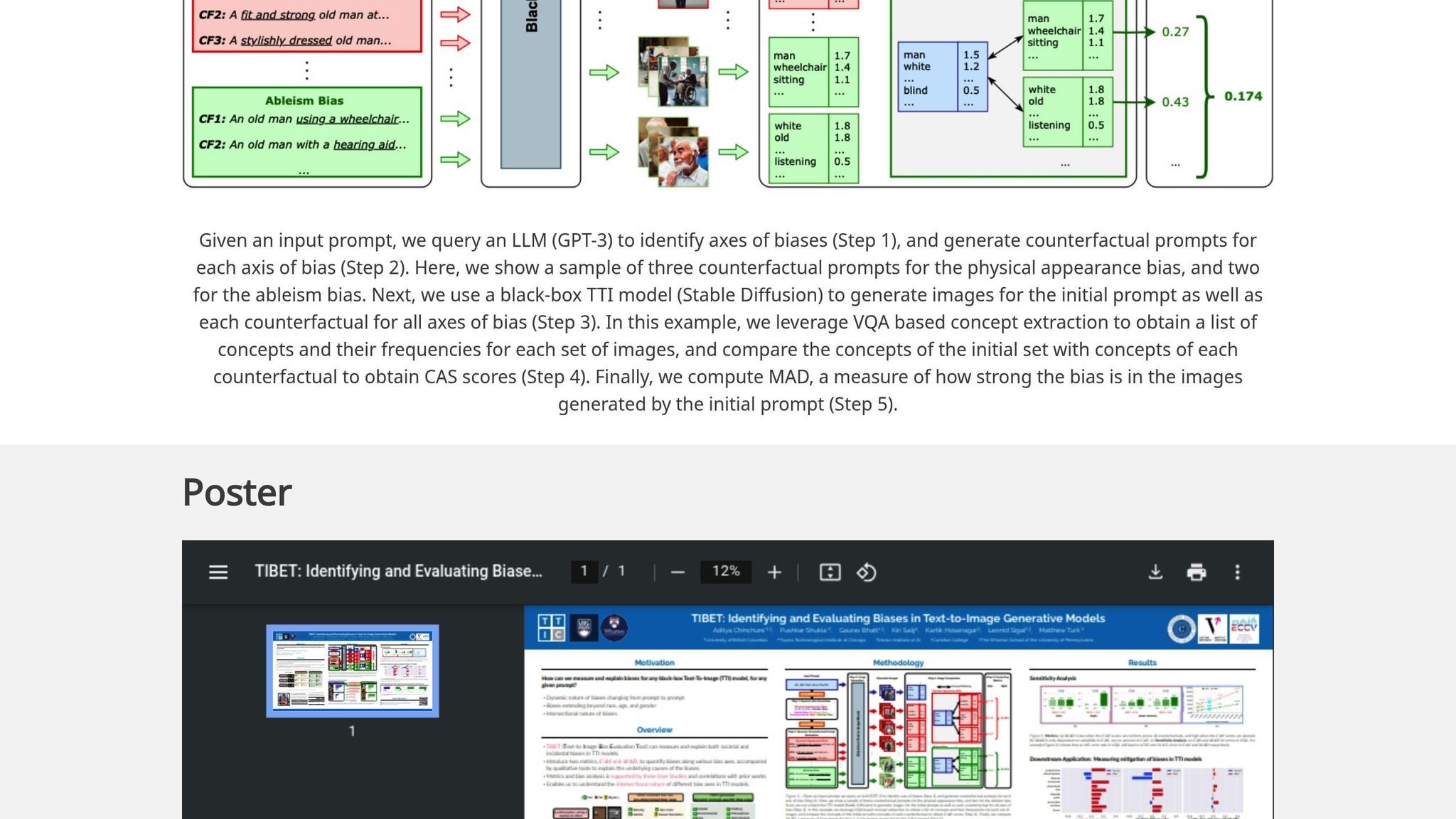
Instead of applying the same checks across all scenarios, TIBET dynamically adjusts its analysis to fit the prompt. For instance, when given the prompt "computer programmer", TIBET generates variations such as "female computer programmer" or "older computer programmer." By comparing these outputs, it identifies potential biases. This nuanced method is particularly suited for the complexities of text-to-image models and complements earlier tools by addressing their limitations.
Using counterfactual analysis and similarity scoring, TIBET can uncover subtle biases, such as a tendency to generate mostly young, male computer programmers. A study by Wharton and the Toyota Technological Institute confirmed its effectiveness. The tool works by creating multiple variations of a prompt with different demographic attributes and then assessing the similarity between the generated images. If significant differences emerge, TIBET flags the bias and assigns a score. However, its accuracy depends on the quality and diversity of the model's training data, and more intricate prompts can sometimes pose a challenge for its analysis.
TIBET stands out with its detailed reporting. It documents the counterfactual prompts used, explains the similarity metrics applied, and provides the reasoning behind each bias score. These reports include both the prompts and their resulting images, making the findings accessible to technical teams and non-technical stakeholders alike. This level of detail is invaluable for documenting bias mitigation steps and meeting audit requirements.
TIBET integrates seamlessly with text-to-image models like Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, and DALL-E through APIs or command-line interfaces. It also supports real-time bias monitoring, allowing developers to analyze images as they are generated. For teams working with NanoGPT's image generation models, TIBET offers a flexible and unified bias detection layer that operates smoothly across various AI systems.
TIBET provides thorough documentation and audit trails to record the entire bias detection process, including corrective actions. It emphasizes privacy by enabling local data storage and processing, ensuring sensitive data remains on the user's device and reducing the risk of breaches. This approach helps organizations meet stringent privacy regulations, particularly when dealing with sensitive image data or operating in highly regulated environments. By combining advanced bias detection with strong privacy safeguards, TIBET reinforces the importance of fairness and accountability in AI-driven image generation.
Bias detection tools come with their own sets of strengths and limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for organizations to choose the right tool based on their technical expertise, compliance needs, and operational goals.
IBM AI Fairness 360 stands out with its extensive fairness metrics and bias mitigation capabilities that span the entire machine learning pipeline. However, it has a steep learning curve and requires advanced machine learning expertise, which can pose challenges for teams without dedicated specialists.
Fairlearn excels in providing detailed metrics and visualizations for both group and individual fairness. Its seamless integration with scikit-learn and Azure ML makes it especially useful for Python-based projects and academic research. That said, its reliance on advanced machine learning knowledge can limit its accessibility for less technical teams.
The Google What-If Tool offers an intuitive, interactive, and code-free interface, making it ideal for educational purposes and model debugging. However, its dependency on Google’s ecosystem restricts offline use and creates reliance on cloud infrastructure.
Aequitas is tailored for regulatory compliance and audit needs, offering detailed reporting features to help organizations meet U.S. standards. It supports both command-line and web-based interfaces to suit different user preferences. On the downside, it lacks real-time bias detection and is more suited for academic and compliance-focused applications.
TIBET is designed to address the unique challenges of text-to-image models with its context-aware analysis. It adapts to specific prompts, making it highly effective for AI image generators. Its strong privacy features and detailed reporting make it ideal for sensitive applications, though its accuracy heavily depends on the quality of the training data.
Here’s a quick comparison to help guide your decision:
| Tool | Key Strengths | Primary Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| IBM AI Fairness 360 | Extensive metrics, broad ML pipeline integration, open-source | Steep learning curve, requires advanced expertise |
| Fairlearn | Detailed fairness metrics, Python-friendly, integrates with Microsoft tools | Needs solid ML knowledge |
| Google What-If Tool | User-friendly, code-free, great for education | Tied to Google ecosystem, limited offline use |
| Aequitas | Compliance-focused, audit-ready reports, intersectional bias analysis | No real-time detection, geared toward academic/policy needs |
| TIBET | Context-aware for images, privacy-focused, adaptable | Performance depends on training data, newer framework |
Choosing the right tool often depends on your team’s technical resources and priorities. Teams with strong machine learning expertise might prefer the robust capabilities of IBM AI Fairness 360 or Fairlearn. Meanwhile, organizations seeking simplicity may gravitate toward the Google What-If Tool. For those focused on compliance, Aequitas provides the necessary audit trails, while TIBET offers a specialized solution for AI image generation workflows, prioritizing privacy and adaptability.
As Gartner predicts generative AI will account for 10% of all data, selecting a suitable bias detection tool is becoming increasingly crucial. For teams managing multiple AI models, such as those on platforms like NanoGPT, TIBET’s ability to provide unified bias detection across various image generation systems - while maintaining local data privacy - makes it a compelling choice.
Bias detection tools cater to a range of organizational needs, offering tailored solutions to address fairness and transparency in AI outputs. After examining their performance, usability, and alignment with U.S. standards, clear patterns emerge for different use cases.
For enterprise environments, IBM AI Fairness 360 emerges as a standout choice despite its complexity. Its extensive metrics, seamless integration capabilities, and detailed documentation make it particularly well-suited for organizations requiring rigorous audits and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
On the other hand, Fairlearn is an excellent option for academic researchers and development teams working on prototypes. Its open-source nature, compatibility with Python, and flexible framework make it ideal for exploratory analysis and research projects. Additionally, its visualization tools are especially beneficial for institutions operating on tighter budgets.
For organizations focused on regulatory compliance and policy research, Aequitas proves to be a strong candidate. Its emphasis on intersectional bias analysis and detailed reporting aligns well with the needs of regulatory audits and documentation. However, its academic orientation may pose limitations for real-time applications.
Meanwhile, the Google What-If Tool suits teams prioritizing simplicity and educational purposes. Its interactive, no-code interface is particularly accessible for non-technical stakeholders, though its reliance on the Google ecosystem could be a drawback for organizations with strict data governance policies.
With Gartner forecasting that generative AI will account for 10% of all data by 2025, it's crucial to choose bias detection tools that can evaluate multiple protected attributes and provide clear, explainable results. By aligning your organization's specific needs - whether focused on enterprise-grade analysis, flexible research, or compliance-driven reporting - with the strengths of these tools, you can enhance the fairness and reliability of your AI image generation processes. Ensuring fairness and transparency is a vital step in advancing ethical AI practices.
Tools like TIBET are built to tackle the unique challenges posed by text-to-image AI models, particularly when it comes to spotting and addressing biases in both the input text and the images they generate. These tools work by examining patterns in the data and outputs, flagging potential problems such as stereotypes or the lack of representation for certain groups.
What sets TIBET apart is its emphasis on clarity and user-friendliness, making it a practical choice for developers and researchers alike. It offers actionable feedback to fine-tune models, helping to create outputs that are fairer and more balanced. This is especially crucial in creative fields, where even subtle biases can have a significant influence on the final product.
When selecting a bias detection tool for AI image generators, privacy and compliance should be at the top of your list. Opt for tools that store data directly on your device instead of relying on cloud storage. This approach keeps your information secure and minimizes potential exposure.
Also, make sure the tool doesn’t use your data to train its models unless you’ve given clear, explicit consent. This ensures your data remains under your control.
Focusing on these factors not only safeguards sensitive information but also supports ethical AI practices, offering you greater transparency and control over your process.
Bias in AI image generation is a pressing issue that organizations must tackle head-on. Why? Because unchecked bias can lead to unfair outcomes, reinforce harmful stereotypes, and erode trust in AI systems. When AI systems misrepresent or discriminate, the impact can ripple across individuals and entire communities, causing real harm.
One way to combat this is through the use of bias detection tools. These tools are essential for promoting fairness in AI-generated visuals. They help identify and address biases, ensuring that the system operates transparently and performs more effectively. Beyond technical benefits, they also help organizations meet ethical standards and align with societal values, making their AI systems more responsible and trustworthy.