Jan 9, 2026
Want to automate smarter? Combining AI models like ChatGPT with RPA tools such as UiPath or Automation Anywhere enables systems that both "think" and "act." AI handles unstructured data (e.g., text or images), while RPA performs repetitive, rule-based tasks. Together, they streamline processes like email classification, invoice processing, and resume screening.
Key steps:
This synergy improves efficiency and reduces manual effort across complex workflows.
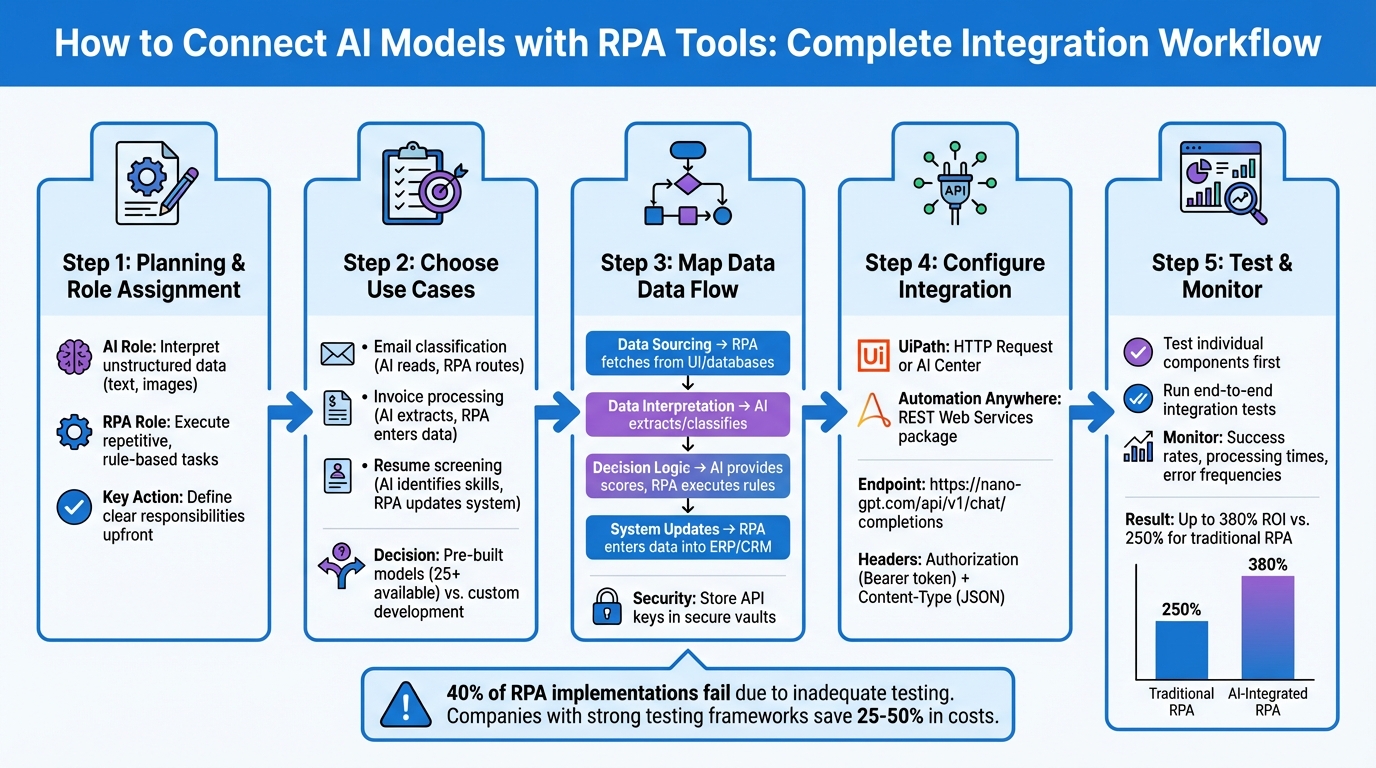
AI and RPA Integration Workflow: 5-Step Process from Planning to Deployment
When integrating AI and RPA, it's crucial to assign clear roles to each. AI excels at interpreting unstructured data, while RPA handles repetitive, rule-based operations like data entry or system updates. By defining these responsibilities upfront, you can streamline workflows and identify potential bottlenecks early on.
To get started, focus on scenarios where unstructured data meets repetitive tasks. For example:
A real-world example: Mediba implemented AI-powered robots to filter inappropriate keywords on its web portal, eliminating the need for manual reviews.
When selecting use cases, decide whether pre-built AI models meet your needs or if custom development is required. Tools like UiPath AI Center offer more than 25 ready-made models for tasks like document understanding, language analysis, and image recognition. These pre-built solutions are ideal for common tasks such as processing utility bills or detecting product defects. For more specialized needs, custom models may be necessary.
After identifying a use case, map out the data flow from input to output. Start by pinpointing the source of your input data - whether it’s a scanned document, an email attachment, or a database query. Next, outline the transformations performed by AI (e.g., extraction, classification, or text generation) and the subsequent actions handled by RPA (e.g., data entry, file movement, or system updates).
Take claims processing as an example: RPA extracts an email attachment, AI analyzes the image, and RPA updates the CRM with the classification results.
To simplify updates and enhance security, centralize API authentication. Store sensitive information like AI API keys in secure vaults or system environment variables.
| Workflow Component | RPA Responsibility | AI Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Data Sourcing | Fetch from UI, databases, or files | N/A |
| Data Interpretation | N/A | Extract fields, classify content, generate text |
| Decision Logic | Execute rule-based if/then paths | Provide probabilistic scores and labels |
| System Updates | Enter data into ERP/CRM systems | N/A |
With workflows mapped, the next step is preparing for robust error handling.
Error handling is an essential part of workflow design. AI models often return confidence scores with their predictions. Use these scores to trigger human reviews for low-confidence results. For instance, if an invoice extraction model has a confidence score below 85%, route that document to a human reviewer instead of processing it automatically. This approach not only prevents errors but also improves model accuracy through human feedback.
Additionally, design workflows to handle API errors gracefully. Include retry logic with exponential backoff and create alternate processing paths for cases when API calls fail. A health insurance company partnered with Amitech Solutions to streamline clinical outcomes using AI Center and Document Understanding. By embedding robust error-handling mechanisms, they achieved significant time and cost efficiencies.
To ensure reliability, validate AI models using evaluation pipelines. Test the model against a dataset to measure metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall. This step helps identify potential issues before deployment and sets performance benchmarks for monitoring data drift over time.
After the planning phase, UiPath provides two primary ways to integrate AI models into your workflows: direct API calls using HTTP Request activities and managed deployments through UiPath AI Center. These methods align with the workflow logic previously discussed. The HTTP Request approach is best for simple integrations where you send prompts to an AI model and get responses. On the other hand, AI Center offers a centralized platform to deploy, manage, and monitor machine learning models within your automation workflows.
To connect NanoGPT's AI models via HTTP requests, start by installing the UiPath.WebAPI.Activities package in UiPath Studio's Manage Packages window. Then, insert an HTTP Request activity into your workflow and configure it to send POST requests to NanoGPT's API endpoint.
Set the method to POST and use the following endpoint:
https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1/chat/completions
Add the required headers:
In the request body, include parameters such as:
To handle JSON data efficiently, import the Newtonsoft.Json and Newtonsoft.Json.Linq namespaces into your workflow. Use JObject.Parse(strResponse) to extract the needed data from the response. If the AI model generates large or complex responses, consider increasing the timeout period in the HTTP Request activity to avoid premature failures.
This method sets up a direct API call, creating a foundation for more advanced integrations.
For a more structured and scalable approach, UiPath AI Center is a great alternative to direct HTTP requests. It acts as a hub for deploying and managing machine learning models within your RPA workflows. You can connect external platforms like NanoGPT using the UiPath Integration Service with the "OpenAI V1 Compliant LLM" connector. This method ensures secure authentication and simplifies the integration process.
Once connected, the external model becomes available as an ML Skill that you can easily drag and drop into your UiPath Studio workflows. This eliminates the need for manual HTTP request configurations for every automation. NanoGPT's OpenAI-compatible API streamlines the process, and with access to over 200 AI models for text, image, and video generation, you can select the best model for your specific needs.

When setting up HTTP Request activities for NanoGPT, use the following settings:
| HTTP Activity Field | NanoGPT Configuration |
|---|---|
| Request Method | POST |
| Endpoint URL | https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1/chat/completions |
| Accept Responses as | JSON |
| Headers | Authorization: "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" Content-Type: "application/json" |
| Parameters (Body) | model: "gpt-4" (or desired model) messages: array of message objects max_tokens: 500 temperature: 0.7 (optional) |
| Response Content | str_ResponseOutput (String variable) |
Before starting the integration, make sure to generate your NanoGPT API key at nano-gpt.com. This key is essential for authenticating your requests and accessing the AI models.
Automation Anywhere allows you to integrate AI models through its REST Web Services package in Automation 360. This setup connects NanoGPT's AI capabilities directly into your bots using standard HTTP requests, giving you control over how workflows interact with AI models.
To integrate NanoGPT, open your bot in Automation 360 and locate the REST Web Services package in the Actions panel. Drag the REST action into your workflow and configure it to send POST requests to NanoGPT's endpoint: https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1/chat/completions.
In the REST action configuration, ensure the Method is set to POST and include these two key headers:
Content-Type: application/json to define the data format.Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY for authentication. (Store your NanoGPT API key securely in the Automation Anywhere Credential Vault instead of hardcoding it.)Use the JSON package to dynamically construct the request body. Set the stream parameter to false to receive the full response in one go. When the API call is executed, the AI-generated content will be available in the response under choices[0].message.content. You can extract this data using the JSON package's "Get node value" action.
For tasks that require real-time information, NanoGPT offers an online search feature. Add :online to your model name (e.g., chatgpt-4o-latest:online) for basic web searches at $0.006 per request. For more in-depth research, use :online/linkup-deep at $0.06 per request.
To make your integration more adaptable, use variables for dynamic configuration. For example:
For instance, you could define a variable $vModelName and set it to chatgpt-4o-latest for standard text tasks. If you need image generation, update the variable to reference the appropriate model and switch the endpoint to https://nano-gpt.com/v1/images/generations.
Store the base API URL in a global variable to simplify updates when the API version changes. Managing HTTP headers with a Dictionary variable makes it easier to update or add authentication tokens across multiple REST actions. Additionally, set a timeout variable to prevent crashes when processing complex requests.
Include error handling (Try-Catch) to manage potential issues like rate limits or server errors. This ensures your bot remains operational even if the API encounters disruptions.
To configure the integration correctly, it's crucial to understand how Automation Anywhere fields align with NanoGPT's API parameters. The table below outlines the mapping:
| Automation Anywhere Field | NanoGPT API Parameter | Example Value / Variable |
|---|---|---|
| URI | Endpoint URL | https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1/chat/completions |
| Method | HTTP Method | POST |
| Header: Authorization | Bearer Token | Bearer $vNanoGPT_Key |
| Header: Content-Type | Content Type | application/json |
| Request Body: model | model |
$vModelName (e.g., chatgpt-4o-latest) |
| Request Body: messages | messages |
[{"role": "user", "content": "$vInputData$"}] |
| Request Body: temperature | temperature |
$vTemperature (0 to 2, controls creativity) |
| Request Body: max_tokens | max_tokens |
$vMaxTokens (limits response length) |
| Request Body: stream | stream |
false (for complete responses) |
| Response Body | Output Content | $vAIResponse |
For image generation, update the URI to https://nano-gpt.com/v1/images/generations and include parameters like prompt, n (number of images), and size (e.g., 1024x1024). NanoGPT's pricing is flexible, starting at $1.00 for standard deposits or $0.10 for cryptocurrency payments, making it affordable to experiment with different models and configurations.
Before deploying your bot, generate your API key at nano-gpt.com and test the connection with a simple prompt. This step ensures your authentication is set up correctly and helps you familiarize yourself with the response structure before building more advanced workflows. Once everything is mapped, test your setup to fine-tune performance.
Start by testing each component individually. For example, with NanoGPT, you can send a test prompt like "Summarize this invoice" to ensure it responds correctly and that authentication works as expected. Pay close attention to how data is passed through variables to confirm accuracy.
Once individual components are verified, move on to integration testing. This step ensures smooth data flow between your RPA tool and the AI model. Conduct end-to-end tests using both valid and invalid data to check for seamless error handling. Skipping thorough testing is a common mistake - nearly 40% of RPA implementations fail for this reason.
Use realistic test data that reflects actual production scenarios, including edge cases like improperly formatted dates, special characters, or excessively long text strings. Companies with strong testing frameworks often save 25% to 50% in costs because their bots perform correctly from day one. Finally, set up regression testing to identify issues when NanoGPT updates its models or when you tweak your RPA workflows. This ensures long-term stability and reliable performance.
To understand how your integration performs in real-world situations, monitor operational metrics like execution success rates, processing times, and error frequencies. RPA platforms often provide dashboards to track these metrics. For NanoGPT, keep an eye on response times and accuracy to spot any performance dips.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as accuracy, exception rates, and cost per transaction are essential to measure. With the global AI-in-RPA market growing at 32.5% annually through 2033, optimizing performance is becoming increasingly important. Implement centralized logging to consolidate all bot operations and AI responses. This historical data helps identify trends, locate bottlenecks, and calculate ROI. Notably, AI-enhanced RPA can achieve up to 380% ROI compared to 250% for traditional RPA. Effective monitoring not only ensures reliability but also supports continuous improvement.
To handle temporary failures, implement retry logic with adjusted timeouts. For instance, if a NanoGPT API call times out, wait a few seconds and try again before escalating the issue.
Introduce human-in-the-loop checkpoints for tasks requiring judgment. Use monitoring tools to flag exceptions that may need manual review. As Mia Urman, CEO of AuraPlayer, puts it:
"The major value and ROI of RPA will come from implementing stability. The goal is to establish automations that are not prone to instability or rapid changes".
Prepare for unexpected issues by developing fallback options. If the AI model becomes unavailable, ensure that work in progress is saved, notify your team automatically, and queue the task for later processing. Additionally, safeguard your NanoGPT API key by storing it securely in your RPA platform's credential vault and rotating it periodically. Regularly test your error-handling mechanisms to confirm your workflows remain resilient, even when challenges arise.
To get started, first generate your NanoGPT API key and verify your account balance. Once that's done, establish the connection within your RPA platform. For UiPath, use the Integration Service, and for Automation Anywhere, rely on REST actions to authenticate using your API key.
Next, design your workflow by leveraging activities like "Generate Chat Completion" or "HTTP Request" to interact with the AI model. Make sure to map your data flow properly - define input arguments for prompts and output arguments for model responses. For added security, store API keys as system environment variables. Finally, integrate with OpenAI-compatible endpoints to connect seamlessly with your RPA connectors. This process ensures a smooth integration, improving operational efficiency and reliability.
Now that the integration process is outlined, let’s look at how NanoGPT can enhance your automation workflows.
NanoGPT simplifies AI integration by offering unified access to multiple models through a single API key. Instead of juggling multiple subscriptions or configurations, you can easily switch between models by adjusting the "model" parameter in your HTTP request. This is all managed through NanoGPT's OpenAI-compatible base URL: https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1.
The platform’s pay-as-you-go pricing model is another standout feature. There are no monthly subscription fees, making it perfect for low-volume or experimental workflows. You can get started with as little as $1.00 (or $0.10 via cryptocurrency), allowing you to test various models without committing to long-term plans.
For workflows requiring real-time data, NanoGPT offers real-time web search capabilities. By appending ":online" to the model name, you can access up-to-date information with a 10x improvement in factual accuracy. Additionally, when handling sensitive data, NanoGPT provides TEE-backed models, allowing you to fetch attestation reports via the /api/v1/tee/attestation endpoint. This ensures data privacy and integrity while keeping all data stored locally on your device, safeguarding your business information throughout the automation process.
When integrating AI models with RPA tools like UiPath, securely storing API keys is essential. UiPath provides built-in secret management features to make this process safer. One effective method is creating a credential asset in UiPath Orchestrator. This ensures your API key is encrypted and accessible only to authorized processes. In your workflows, you can reference this asset using the Get Credential activity, keeping the key hidden from plain view.
For added security, consider using Personal Access Tokens (PATs) instead of raw API keys. PATs allow for scoped and revocable access, making them a safer alternative. Store these tokens just like API keys to maintain security standards. Avoid hard-coding keys in your workflows, limit access to only necessary users or robots, and regularly rotate keys or tokens - ideally every 90 days. These steps help safeguard your credentials and ensure a secure integration between AI models and RPA tools.
Integrating AI models like ChatGPT or DALL-E with RPA tools such as UiPath or Automation Anywhere can simplify and enhance various workflows. One common application is natural language processing (NLP), where AI helps RPA bots handle tasks like drafting emails, summarizing lengthy documents, or organizing unstructured text. For instance, a bot could use AI to craft customer responses and send them through the correct system automatically.
Another valuable use is intelligent document processing. Here, AI extracts key data from sources like invoices, contracts, or support tickets. This allows bots to classify information, identify errors, and seamlessly feed clean data into platforms like ERPs or CRMs. AI also supports workflows such as sentiment analysis, which helps prioritize tasks or escalate issues based on urgency or tone.
Generative image models, such as DALL-E, open up even more possibilities by creating visual assets on demand. These could include marketing graphics, product mock-ups, or personalized certificates, all of which can be saved or distributed automatically. By combining AI with RPA tools, businesses can achieve smarter, more efficient automation solutions that save time and effort.
Effectively managing errors is crucial for keeping AI and RPA workflows dependable. When it comes to RPA processes, the first step is to standardize error codes. This ensures that any failures are reported in a consistent way, making it much simpler to analyze and address issues. Incorporating real-time monitoring allows you to catch exceptions as they happen, whether they stem from business-related problems like rule violations or technical issues such as UI changes disrupting a sequence. Every incident should be logged with all relevant details - think input data, bot status, and more. From there, an exception-resolution workflow can handle errors appropriately by retrying, pausing for manual review, or safely aborting operations depending on the nature of the problem.
For AI workflows, a proactive approach to error management is essential. Start by minimizing errors through the use of high-quality training data and by fine-tuning models locally to maintain privacy. Confidence scores can help you identify low-confidence outputs, triggering a human-in-the-loop review when necessary. To consistently improve accuracy, resolved errors should be fed back into the model’s training process. By blending RPA’s structured error-handling methods with AI’s confidence-based safeguards, you can build a robust system that minimizes downtime, secures data, and adapts effectively as it scales.