Jan 31, 2026
Dynamic load balancing is a game-changer for energy efficiency in AI workflows. By redistributing tasks across servers in real time, it prevents some servers from being overburdened while others remain idle. This approach reduces energy waste, lowers operational costs, and ensures efficient use of resources.
Dynamic load balancing is transforming AI data centers into efficient, energy-conscious operations by reallocating resources based on demand.
To set up dynamic load balancing, you'll need a solid toolkit. At the heart of this process is Kubernetes, which excels at task orchestration. Pairing Kubernetes with Dynamic Resource Allocation (DRA) makes it possible to adjust GPU resources on the fly without disrupting running workloads. Meanwhile, CloudSim offers a simulated data center environment, letting you test load-balancing algorithms in a controlled setting before deploying them in production.
For AI-specific energy management, DynamoLLM is a go-to framework for managing LLM inference clusters. It dynamically tweaks GPU frequency and model parallelism to reduce energy consumption and costs while maintaining latency targets. On top of that, tools like NVIDIA Domain Power Service (DPS) provide SDKs and command-line utilities such as dpsctl to simulate power-shedding scenarios and manage resource lifecycles. These tools collectively help map workflow dependencies with precision, ensuring a more efficient setup.
AI workflows are rarely simple or isolated. They often involve tasks that are dependent on one another, forming parent-child relationships where some tasks must be completed before others can begin. A common way to map these dependencies is through Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), a structure already utilized by tools like Apache Airflow, AWS Batch, and Azure Batch.
To take it a step further, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) can be applied to these dependency maps. Unlike traditional neural networks, GNNs capture intricate structural relationships, enabling smarter and more efficient scheduling decisions. This approach significantly improves the makespan, or the total time required to complete a workflow, compared to older scheduling methods.
A key strategy here is to identify tasks with high dependency counts or long execution times during preprocessing. By assigning these tasks to separate queues, you can avoid system-wide bottlenecks and keep workflows running smoothly.
A deep understanding of AI algorithms is essential for implementing dynamic load balancing. Reinforcement Learning (RL) methods, such as Q-learning, Deep Q-Networks (DQN), and Actor-Critic models, are particularly useful for learning optimal scheduling policies. These algorithms allow systems to adapt to changing workloads in real time. For example, in early 2025, researchers introduced the RL-MOTS framework, which used a Deep Q-Network on a simulated cloud platform to cut energy usage by 27% compared to leading metaheuristic methods.
Beyond RL, knowledge of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) can help predict workloads. A study from March 2024 demonstrated a dynamic load-balancing model that combined CNNs and RNNs to calculate virtual machine (VM) loads. This model used a mix of optimization and reinforcement strategies to classify VMs by their load levels.
Additionally, understanding metaheuristic optimization algorithms like Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Genetic Algorithms (GA) is invaluable. These methods are often paired with AI to explore large search spaces for resource allocation, making them a cornerstone of energy-efficient load-balancing techniques. Mastering these algorithms opens the door to creating smarter and more sustainable systems.
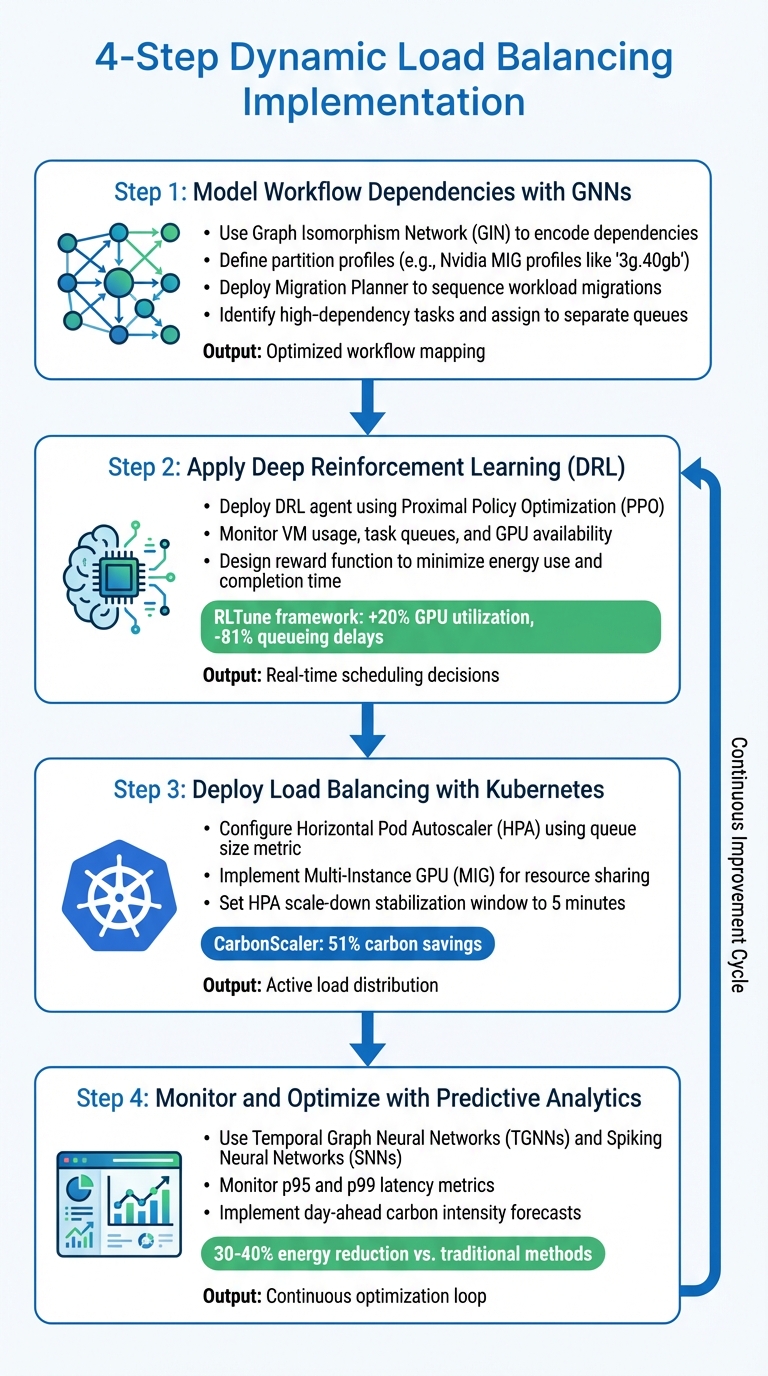
4-Step Dynamic Load Balancing Implementation Guide for AI Workflows
Start by extending the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) method to better capture workflow complexity. Use a Graph Isomorphism Network (GIN) to encode dependencies effectively.
Define partition profiles for each workload. For instance, Nvidia MIG profiles like 3g.40gb specify the exact compute and memory resources required for a task. A Migration Planner then sequences workload migrations across the cluster, ensuring smooth transitions. By identifying high-dependency tasks and long-running operations during this preprocessing phase, you can assign them to separate queues, reducing bottlenecks.
Once dependencies are modeled, move on to optimizing your scheduling process.
Next, deploy a Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) agent using Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) to make real-time scheduling decisions. The DRL agent monitors the current state of your cloud environment - such as VM usage, task queues, and GPU availability - and selects actions to improve both energy efficiency and performance. Unlike static scheduling, this approach dynamically adapts to changing workloads without requiring prior knowledge of all tasks.
Design a reward function that discourages excessive energy use and long task completion times. In December 2025, researchers introduced RLTune, an RL-based framework trained on real-world traces from Microsoft Philly, Helios, and Alibaba. This system improved GPU utilization by 20% and reduced queueing delays by 81%. The feedback loop ensures that the agent continuously refines its decisions, making the system increasingly efficient over time.
Once your scheduling policies are optimized, implement them using Kubernetes. Configure Kubernetes to translate DRL-based decisions into container redistributions. Leverage the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), using queue size as the primary metric since it aligns with request latency and supports diverse workloads. Additionally, use Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) to partition GPUs, enabling efficient resource sharing across models.
A practical example of this is the CarbonScaler project, introduced in October 2023 by researchers including Walid A. Hanafy and Prashant Shenoy. This system utilized a greedy algorithm for "carbon scaling", dynamically adjusting server allocations based on grid carbon intensity. Testing on real machine learning training jobs demonstrated 51% carbon savings compared to standard execution methods. For better stability, set the HPA scale-down stabilization window to five minutes to avoid unnecessary fluctuations.
To maintain energy efficiency, integrate predictive analytics into your system. Use Temporal Graph Neural Networks (TGNNs) and Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) to forecast resource availability and workload trends, enabling proactive task placement.
Monitor p95 and p99 latency metrics to keep an eye on performance. Studies show that combining TGNNs with SNNs can cut energy consumption by 30–40% compared to older methods. Google's Carbon-Intelligent Compute Management system is a great example - it uses day-ahead carbon intensity forecasts to create Virtual Capacity Curves, delaying flexible workloads to times when the energy grid is cleaner. This continuous monitoring loop ensures resources are allocated efficiently while maintaining peak performance.
When comparing static and dynamic load balancing, their differences in energy efficiency and adaptability become clear.
Static load balancing relies on fixed rules like round-robin or least-connections methods. While straightforward, this approach tends to over-provision resources, leading to wasted energy. It keeps a large buffer of idle capacity to handle peak demand scenarios, even when such demand is rare. On the other hand, dynamic load balancing leverages real-time telemetry and AI-driven algorithms to allocate resources based on current needs. This ensures that energy consumption aligns closely with actual demand.
The energy benefits of dynamic load balancing are impressive. For example, Google's DeepMind RL agent achieved a 40% reduction in cooling energy and improved the Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) metric by 15%. Similarly, Microsoft Azure and Alibaba Cloud reported energy reductions of 10% and 8%, respectively.
| Feature | Static Load Balancing | Dynamic Load Balancing |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Low; over-provisions for peak demand | High; cuts consumption by 15–25% through real-time adjustments |
| Flexibility | Rigid; relies on fixed settings | High; uses tools like "Flex Tiers" and workload tagging |
| Response Type | Reactive; adjusts after performance issues | Predictive; anticipates spikes using AI |
| Use Cases | Suitable for legacy systems with stable workloads | Ideal for hyperscale data centers and AI applications |
Dynamic load balancing clearly outshines its static counterpart in efficiency and adaptability. Next, let's look at the AI techniques that power its performance.
AI technologies underpin the success of dynamic load balancing by providing precision and adaptability. Different techniques offer unique strengths. For instance, reinforcement learning (RL) excels in adaptability, while long short-term memory (LSTM) models shine in forecasting accuracy. In energy demand forecasting scenarios, LSTM achieved a mean absolute error (MAE) of 21.69, far better than ARIMA (87.73) and Prophet (59.78).
| Technique | Energy Savings | Responsiveness | Workload Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Learning (RL) | ~40% (Cooling/Power) | Highly adaptable; operates autonomously | Real-time, dynamic environments |
| LSTM (Deep Learning) | High precision | MAE: 21.69 (best accuracy) | Complex, non-linear time-series data |
| Gradient Boosted Trees | ~10% | High short-term forecasting accuracy | Short-term load forecasting |
| ARIMA / Prophet | Moderate | MAE: 59.78–87.73 (lower accuracy) | Linear or simple seasonal patterns |
One standout example is the DynamoLLM framework, which dynamically reconfigures large language model (LLM) inference clusters. This approach saved 53% in energy usage and cut operational carbon emissions by 38%. These results underscore how AI-driven dynamic systems consistently outperform static methods in energy efficiency, responsiveness, and adaptability to varying workloads.
Dynamic load balancing delivers impressive results: 53% energy savings, 38% lower carbon emissions, and up to 61% reduced operational expenses.
Take the Emerald AI trial in Phoenix as an example. By implementing dynamic load balancing on a 256-GPU cluster during peak usage, power consumption dropped by 25%. This approach transforms data centers from passive energy consumers into active participants in the energy grid, adapting to real-time demand.
Additionally, findings from ReGate reveal that 30%–72% of NPU energy is wasted through static dissipation. Power-gating idle components can recover this energy. By consolidating workloads, organizations can stretch the value of their existing hardware while slashing their carbon footprint. These advancements set the stage for more efficient, environmentally conscious load balancing strategies.
The future of dynamic load balancing will see even deeper integration with power grids and renewable energy sources. One promising development is carbon-aware scheduling, which shifts non-essential AI tasks to periods when renewable energy, like solar or wind, is abundant. This strategy could potentially unlock up to 100 GW of additional data center capacity in the U.S., all without requiring new power plants or transmission infrastructure.
Hardware innovations will also play a critical role. Researchers Yuqi Xue and Jian Huang from the University of Illinois emphasize:
"As the feature size continues to shrink in the future, supporting flexible power management is highly desirable for a sustainable NPU chip design".
Advances like extending ISAs to allow compilers to control individual power states will push efficiency to new heights.
For organizations looking to adopt dynamic load balancing, a good starting point is categorizing AI workloads by their flexibility. Real-time inference tasks, for instance, require strict performance guarantees (Flex 0), while batch training jobs can handle up to 50% performance variability (Flex 3). This classification enables smarter throttling, balancing energy savings with service reliability. Combining reactive scaling with proactive scheduling creates a solid framework for sustainable AI operations. Together, these advancements promise to reshape how AI and renewable energy work hand in hand.
Dynamic load balancing helps conserve energy in AI workflows by smartly allocating tasks across resources based on real-time needs. It fine-tunes system settings - like the number of active instances, model parallelism, and GPU usage - to maintain energy efficiency while keeping performance intact.
This method cuts down on excess power usage by activating resources only when they're required, which reduces energy waste and carbon emissions. By adjusting to changing workloads, dynamic load balancing promotes a more efficient and eco-friendly approach to managing AI operations.
AI algorithms play a key role in improving load balancing by enabling smarter, more responsive resource management. Through predictive analytics, AI can evaluate both historical and real-time data to anticipate system demands. This allows for proactive adjustments in resource allocation, helping to avoid bottlenecks and maintain smoother operations.
AI models, such as those based on reinforcement learning, take optimization a step further. They dynamically adjust workload distribution by analyzing current system performance in real time. In energy management, for example, AI uses advanced neural networks and time series analysis to forecast energy demands. This minimizes waste and boosts efficiency.
By tapping into these capabilities, AI not only ensures better use of resources but also supports the development of systems that are more energy-efficient and resilient.
Carbon-aware scheduling helps reduce energy consumption in data centers by timing workloads to coincide with periods when the grid relies on cleaner energy sources. This method cuts down on carbon emissions by ensuring tasks are processed during these environmentally favorable times. It also optimizes resource usage by dynamically managing operations - pausing, resuming, or scaling them based on real-time energy demand and availability - making workflows more efficient and environmentally friendly.