Jan 14, 2026
Integrating AI models with preprocessing tools can simplify data workflows, reduce errors, and save time. This process involves cleaning and transforming raw data into a format that AI models can use effectively, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Here's a quick overview of how to set up an automated pipeline:
requests to send preprocessed data to NanoGPT's API, enabling smooth interaction with AI models.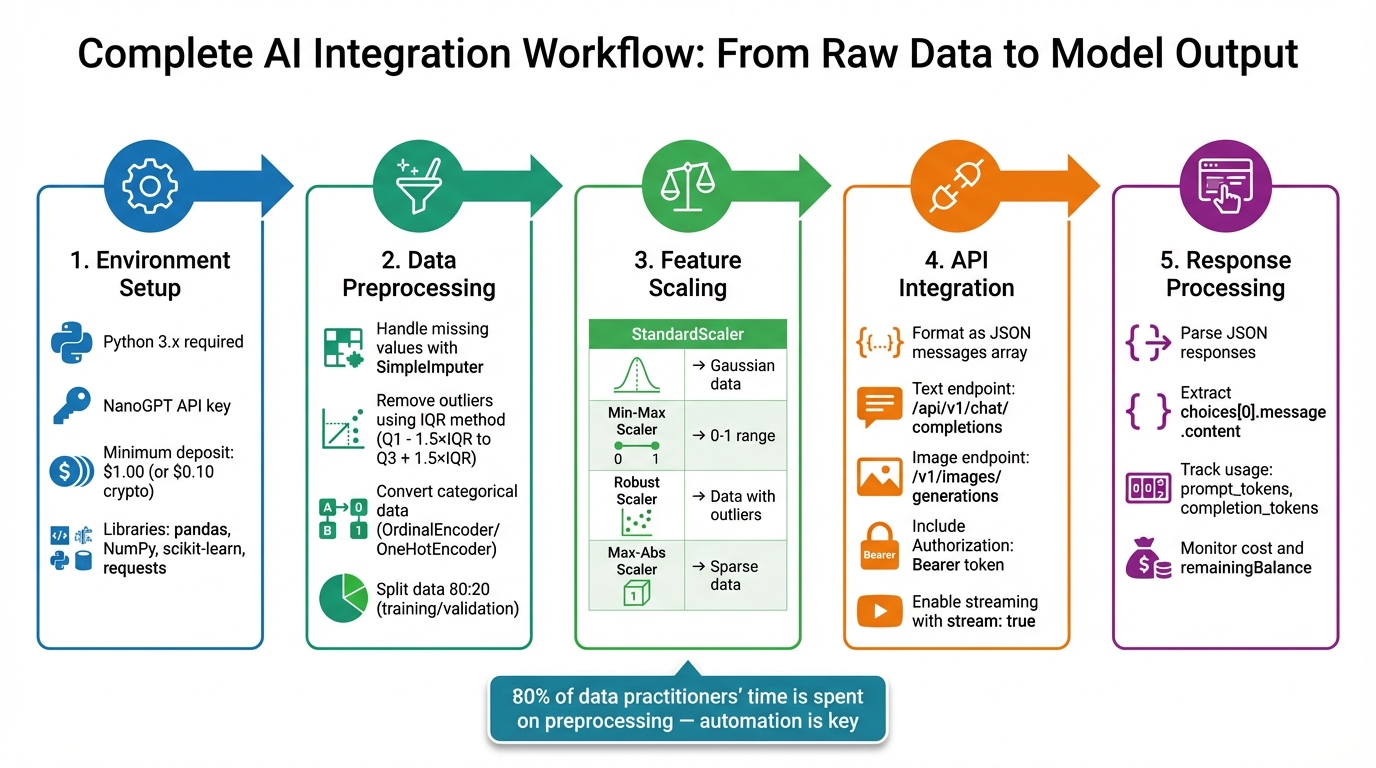
5-Step AI Model Integration Workflow with Preprocessing Pipeline
NanoGPT operates through API calls, making it easy to get started with just a device running Python or Node.js and a steady internet connection. Before diving in, make sure you’ve got all the necessary tools and requirements in place.
To begin, ensure you’re using Python 3.x. You’ll also need a NanoGPT account with an API key, which you can generate from the platform’s API settings page. Keep in mind that NanoGPT requires a prepaid balance to function - $1.00 is the minimum deposit for standard payments, while cryptocurrency users can start with just $0.10. For data preparation, you’ll rely on pandas, NumPy, and scikit-learn. The requests library will handle HTTP POST and GET requests for API communication, while Python’s built-in json and base64 libraries will help parse responses and manage image data.
Once you’ve gathered the prerequisites, it’s time to install the necessary Python libraries. Open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install requests pandas numpy scikit-learn
This step sets up everything you need for data preprocessing and API communication. The requests library is particularly important for making HTTP calls to NanoGPT’s API endpoints, while the others handle data preparation tasks.

To connect NanoGPT to your workflow, you’ll need to configure API access. Start by setting the API base URL to https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1. Then, create an Authorization header using the format Bearer YOUR_API_KEY. For security, store your API key in an environment variable instead of hardcoding it into your scripts.
When making standard JSON requests, include Content-Type: application/json in your headers. If you plan to use Server-Sent Events for streaming responses, add Accept: text/event-stream to your headers and set "stream": true in the data payload. Before sending your first request, double-check that your account has enough funds - NanoGPT won’t process requests if your balance is too low.
Turning raw data into clean, structured input is essential for models like NanoGPT. Tools like pandas, NumPy, and scikit-learn make this process efficient and reliable.
Start by examining your dataset with df.info() and df.isnull().sum(). These commands help identify missing values and data type inconsistencies. To handle missing data, use scikit-learn's SimpleImputer to fill gaps with a mean, median, or constant value. For larger datasets, you might consider dropping rows with missing values if the impact is minimal.
Outliers can distort results, so use the Interquartile Range (IQR) method to detect and remove them. Calculate the bounds as Q1 - 1.5×IQR and Q3 + 1.5×IQR. For categorical data, convert it into numeric form using OrdinalEncoder for ordered categories or OneHotEncoder for unordered ones.
"Clean and well-structured data allows models to learn meaningful patterns rather than noise." - GeeksforGeeks
Feature scaling is crucial to ensure no single feature disproportionately influences the model. Depending on your data, choose the right scaler:
| Scaling Approach | Best Use Case | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| StandardScaler | Gaussian-like data | Centers data at zero with unit variance |
| Min-Max Scaler | Non-distance-based models | Scales features to a range, typically 0–1 |
| Robust Scaler | Data with many outliers | Uses median and interquartile range |
| Max-Abs Scaler | Sparse data | Scales features to the largest absolute value, keeping zeros |
For datasets with outliers, RobustScaler is a better choice. Sparse datasets, on the other hand, benefit from MaxAbsScaler. As the scikit-learn documentation notes:
"Standardization of datasets is a common requirement for many machine learning estimators implemented in scikit-learn; they might behave badly if the individual features do not more or less look like standard normally distributed data." - scikit-learn Documentation
Divide your dataset into training and validation sets using train_test_split, typically with an 80:20 ratio. Always fit transformers (like scalers or encoders) on the training data first, then apply them to the validation set. To streamline this process, use scikit-learn's Pipeline to chain preprocessing steps. This ensures consistency and makes your workflow reproducible.
Once your data is preprocessed, it's ready to be formatted and fed into NanoGPT's API seamlessly.
Once your data is preprocessed, the next step is to format it for NanoGPT's API and retrieve results. With your preprocessed data pipeline ready, you can structure and send the data to NanoGPT's API for interaction. NanoGPT uses OpenAI-compatible endpoints, making it easy to create requests using standard JSON payloads for both text and image generation tasks.
For text generation, your data should be organized as a messages array. Each message object needs two fields: role (which can be "system", "user", or "assistant") and content. Here's an example payload:
{
"model": "chatgpt-4o-latest",
"messages": [
{ "role": "user", "content": "your preprocessed text" }
],
"temperature": 0.7
}
For image generation, include an image description as a prompt along with parameters like dimensions (e.g., 512×512 or 1024×1024). If you're working with images, encode them as a base64 data URL (under 4 MB) in supported formats like PNG, JPEG, WEBP, or GIF.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
model |
String | Model ID (e.g., chatgpt-4o-latest). Suffixes like :online enable web search. |
messages |
Array | List of message objects with role and content. |
imageDataUrl |
String | Base64 data URL for img2img tasks. |
temperature |
Number | Controls randomness (0–2); lower values produce more predictable outputs. |
max_tokens |
Integer | Maximum number of tokens to generate. |
response_format |
String | For images: b64_json (default) or url for signed download links. |
To send requests, include a Bearer token in the header: Authorization: Bearer your_api_key. Use https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1 for text models and https://nano-gpt.com/v1/images/generations for image generation. Below is a Python example using the requests library:
import requests
import json
headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer your_api_key",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"model": "chatgpt-4o-latest",
"messages": [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a data analysis assistant." },
{ "role": "user", "content": "Analyze this preprocessed dataset: [your data]" }
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 500
}
response = requests.post(
"https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1/chat/completions",
headers=headers,
data=json.dumps(payload)
)
result = response.json()
print(result['choices'][0]['message']['content'])
For streaming responses, add "stream": true to your payload and include "Accept": "text/event-stream" in your headers. This enables real-time results via Server-Sent Events (SSE). You can then process each response line by stripping the data: prefix and parsing the JSON chunk to extract delta.content.
NanoGPT operates on a pay-per-request model with no subscriptions. Usage metrics in each response help track costs. These metrics include prompt_tokens, completion_tokens, and total_tokens. You can use this data to monitor spending as you process API responses.
Handling responses depends on whether you're using streaming or non-streaming requests. For non-streaming responses, parse the returned JSON and extract the generated text from the choices array. The content is located in choices[0].message.content. Always check the finish_reason field - "stop" means the generation completed as intended, while "length" indicates the max_tokens limit was reached and may need adjustment.
For image responses, the API may return either a base64 string or a temporary download URL (valid for one hour). If you receive a base64 string, decode it using base64.b64decode() and save it as a file. If the response includes a signed URL, download the image promptly, as it will expire within the hour. NanoGPT retains generated files for 24 hours before deleting them permanently.
For models that support reasoning, a reasoning field may be included in the response. You can control the depth of reasoning with the reasoning_effort parameter, which offers settings like minimal (10% of max tokens), low (20%), medium (default, 50%), and high (80%).
Cost tracking is built into the API responses. For image generation, fields like cost and remainingBalance are included. Logging these metrics after each request can help you manage your budget and set alerts to track usage trends effectively.
Once you've set up your preprocessed pipeline, the next step is automation - covering everything from data transformation to API interaction. With NanoGPT, you can create a fully automated workflow. This includes scripting tasks like data cleaning, converting images to base64, and submitting JSON payloads to NanoGPT's endpoints. Use https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1/chat/completions for text and https://nano-gpt.com/v1/images/generations for images.
To process outputs in real time and reduce latency, enable SSE by including stream: true in your payload. For workflows that need to retain context, you can append :memory to your model name or include the memory: true header, which stores conversation history for up to 30 days.
If your workflow requires pulling in external data or performing specific actions, you can use tool calling. Simply define your functions in the tools array, and the model will generate structured arguments for automated execution by your script. For batch jobs, you can set up the notifications-url parameter to receive status updates via webhooks, creating a hands-off, automated pipeline.
Even with a well-built pipeline, occasional errors are inevitable. Knowing how to handle these issues can keep things running smoothly. For example, if you encounter a 429 error (rate limiting), use exponential backoff - start with a 200ms delay and double it until the request goes through. A 503 error (Service Unavailable) may require retrying later or disabling stickyProvider if cache consistency isn't critical.
Cache inconsistency can be another challenge, especially if NanoGPT's failover system switches backend services, which can invalidate cached tokens. To address this, set stickyProvider: true in the prompt_caching object. While this helps maintain cache consistency, it could also trigger a 503 error if the primary service becomes unavailable.
Here’s a quick reference for common errors:
| Error Code | Meaning | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request | Check for invalid parameters or unsupported image formats. |
| 401 | Unauthorized | Ensure the API key is included in the Authorization header. |
| 413 | Payload Too Large | Compress or resize images to stay under the 4 MB limit. |
| 429 | Too Many Requests | Use exponential backoff. |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | Retry later or disable stickyProvider if necessary. |
Once you've resolved common errors, focus on refining your workflow for better speed and cost efficiency. For text generation, enable streaming to accelerate output delivery. When working with images, compress them before converting to base64 to save time and resources.
To manage costs, take advantage of prompt caching. Cached replays can reduce token expenses by about 90%, although the first use incurs a slightly higher cost - 1.25× for a 5-minute TTL or 2× for a 1-hour TTL. Keep track of your spending by logging the cost and remainingBalance fields included in API responses.
For added security when handling sensitive data, use TEE-backed models (identified with the TEE/ prefix) and automate the retrieval of attestation reports. Always store API keys securely as environment variables (e.g., export OPENAI_API_KEY="your_key") instead of embedding them in your scripts. Finally, remember that signed URLs expire after one hour, and files are automatically deleted after 24 hours - so automate downloads promptly.
Bringing preprocessing tools and AI models together can transform how data workflows operate. On average, data practitioners dedicate around 80% of their time to data preprocessing and management tasks. By streamlining these steps, productivity gets a major boost. Plus, effective integration minimizes the risk of "garbage in, garbage out" issues and cuts down on the computational power needed for training and inference. As Idan Novogroder aptly puts it:
"Your data project will only be as successful as the input data you feed into your machine learning algorithms".
AI becomes truly impactful when it seamlessly integrates into everyday operations. Ramakrishna Sanikommu explains this well:
"AI becomes infrastructure - not innovation theater - only when it quietly augments, integrates, and adapts across the enterprise".
With nearly 80% of companies projected to adopt generative AI by 2026, building efficient preprocessing workflows today ensures you're ahead of the game. These operational improvements align perfectly with the capabilities of NanoGPT.
NanoGPT simplifies the process by offering access to over 200 AI models through a single OpenAI-compatible API. Its flexible pay-as-you-go model allows you to experiment without long-term commitments, with deposits starting as low as $1.00 (or $0.10 if using cryptocurrency).
Privacy is a key focus for NanoGPT, as it doesn’t store prompts or associate them with IP addresses. For sensitive data, you can use TEE-backed models and request attestation reports to ensure your information is handled securely. Additional features like web search integration enhance factual accuracy by up to 10x, and prompt caching can cut token costs by approximately 90% for repeated queries.
With these tools and insights in hand, setting up a streamlined workflow is straightforward. Start by generating an API key on the NanoGPT API page, make your minimum deposit, and configure your code to connect with the appropriate endpoints:
https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1/chat/completionshttps://nano-gpt.com/v1/images/generations If you’re using Python, the LiteLLM library integrates easily with the nano-gpt/ prefix. Begin by testing a single model to evaluate its performance, then expand as needed. Use the /api/v1/models endpoint to explore available options and pricing. For real-time feedback, enable streaming with stream: true, or add :memory to the model name to maintain conversation context. These steps ensure a smooth transition from planning to implementation, allowing you to refine your workflow quickly while balancing performance and cost.
To keep your NanoGPT API key safe, start by generating it in your NanoGPT dashboard and storing it securely - options like environment variables or secret-management tools work well. Avoid embedding the key directly in your source files, as this could leave it vulnerable to unauthorized access.
When using the key in your code, reference it through the environment variable. For instance, include it as an HTTP header when making API requests. To further protect your projects, assign different keys to separate environments or applications, and make it a habit to rotate these keys regularly. This means generating new keys periodically and revoking the old ones. Additionally, monitor your key activity through the NanoGPT dashboard. If you suspect any compromise, revoke the affected key immediately and replace it with a new one.
By following these steps, you can ensure your API key remains secure while seamlessly integrating NanoGPT AI models with your tools.
Handling missing data properly is key to building reliable AI models. To start, examine the pattern of missing data. Are values missing completely at random, at random, or not at random? Understanding this will guide you toward the best approach.
If the missing data is minimal and occurs randomly, you might simply remove the affected rows or columns. But when dealing with larger gaps, imputation becomes essential. Basic methods include filling in missing values with the mean, median, or mode for numerical data, or using the most frequent category for categorical data. For more accurate results, advanced techniques like k-nearest neighbors (KNN) or regression-based imputation can help maintain the relationships between variables.
To maintain consistency, make sure you apply the same preprocessing steps across your training, validation, and production datasets. For example, when working with NanoGPT, you can easily incorporate these preprocessing steps, ensuring your model gets clean, structured data without missing value issues.
To cut down on API costs with NanoGPT, start by refining your data before making API calls. Streamline your inputs by removing unnecessary details, standardizing whitespace, and avoiding repetitive content. This reduces the token count, which directly impacts costs.
Group similar requests together whenever possible to reduce processing overhead. For instance, you can combine multiple prompts into a single API call or cache embeddings locally for repeated use. This eliminates redundant requests and improves overall efficiency.
Lastly, select the smallest model that fits your task. NanoGPT offers various model sizes, so you can opt for lighter, more cost-effective options for simpler tasks while saving the larger models for more demanding queries. By cleaning inputs, batching requests, caching results, and choosing the right model size, you can effectively manage and lower your expenses.