Jan 19, 2026
Want to integrate OpenAI's API with Java? Here's what you need to know:
CompletableFuture.Quick Start:
openai-java SDK (v4.15.0).Responses API for text generation tasks.This guide covers setup, API usage, and advanced features to help you get started efficiently.
To get started with Java and OpenAI's SDK, you’ll need to make sure your system meets the necessary requirements, set up libraries, and securely manage your API credentials. The official openai-java SDK requires Java 8 or higher, but using JDK 11 or later is recommended for better performance and access to modern features. Additionally, you’ll need a build automation tool like Maven or Gradle to handle dependencies. Let’s go over the essentials to ensure your environment is ready.
Before diving in, make sure you have the following:
To integrate the OpenAI SDK, you’ll need to include the dependency for version 4.15.0. Here’s how to add it:
pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.openai</groupId>
<artifactId>openai-java</artifactId>
<version>4.15.0</version>
</dependency>
build.gradle file:
implementation("com.openai:openai-java:4.15.0")
Keep in mind that this SDK is still in beta, meaning some classes - such as those for the Assistants API - may undergo changes in future updates. It’s also worth noting that older community libraries, like Theo Kanning’s openai-java, are no longer maintained (it was archived in June 2024). Stick with the official com.openai library to ensure you receive updates and security patches. Once your dependencies are in place, the next step is to secure your credentials.
Hardcoding your API key is a security risk, especially if your code ends up in a public repository. Instead, store your API key as an environment variable named OPENAI_API_KEY. You can then use the OpenAIOkHttpClient.fromEnv() method to load it. The SDK will automatically read your API key, along with your organization ID and project ID, from these environment variables.
For production environments, consider using professional-grade secret management tools like AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, or Azure Key Vault to handle sensitive credentials securely. Additionally, for better performance, it’s a good practice to create a single shared client instance for all API interactions. Each client instance manages its own connections and thread pools, so reusing one instance is much more efficient than creating new ones for every request.
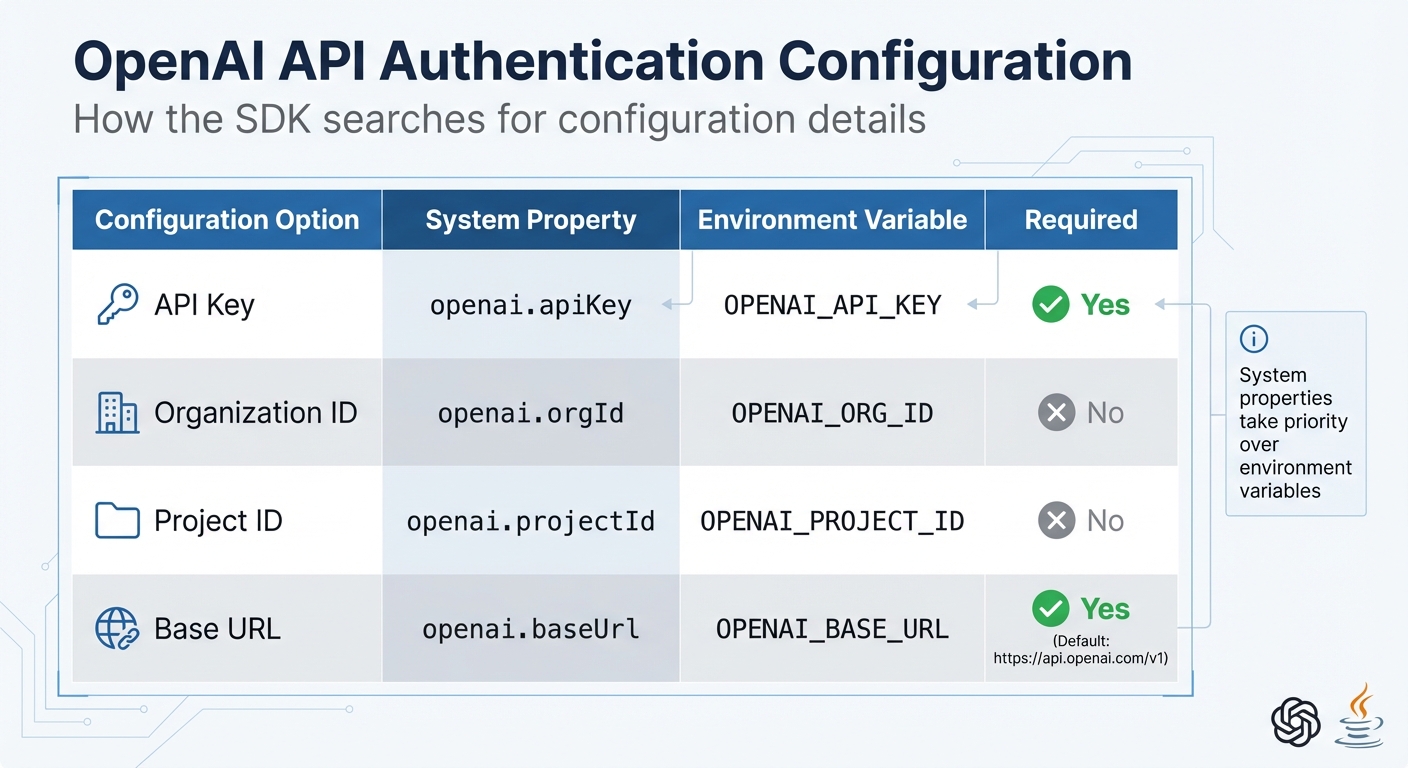
OpenAI API Authentication Configuration Options for Java
Once your setup is ready, you can dive into making API calls. The official com.openai:openai-java SDK takes care of most of the complex tasks like authentication, request formatting, and response parsing. This allows you to focus on developing your application logic without worrying about the underlying details.
Every API request requires authentication through HTTP Bearer tokens (Authorization: Bearer OPENAI_API_KEY). The Java SDK simplifies this by automatically retrieving your API credentials from system properties or environment variables when you initialize the client with OpenAIOkHttpClient.fromEnv(). System properties take priority over environment variables.
Here’s how the SDK searches for configuration details:
| Configuration Option | System Property | Environment Variable | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| API Key | openai.apiKey |
OPENAI_API_KEY |
Yes |
| Organization ID | openai.orgId |
OPENAI_ORG_ID |
No |
| Project ID | openai.projectId |
OPENAI_PROJECT_ID |
No |
| Base URL | openai.baseUrl |
OPENAI_BASE_URL |
Yes (Default: https://api.openai.com/v1) |
If you’re working with multiple organizations or projects, you can include the optional headers OpenAI-Organization and OpenAI-Project to specify the context for billing and resources. Avoid exposing API keys in client-side code; always handle authentication securely on a server. If environment variables aren't an option, you can configure the client manually using a builder pattern:
OpenAIClient client = OpenAIOkHttpClient.builder()
.apiKey("My API Key")
.build();
For better performance, reuse a single client instance across all API calls. This approach helps efficiently manage connection and thread pools. With authentication set up, you’re ready to build requests for generating text.
For new projects, OpenAI suggests using the Responses API instead of the older Chat Completions API. The Responses API is particularly suited for reasoning models like GPT-5. Creating a request is straightforward: define a Params object (e.g., ResponseCreateParams) and pass it to the client’s create method.
Here’s a simple example:
OpenAIClient client = OpenAIOkHttpClient.fromEnv();
ResponseCreateParams params = ResponseCreateParams.builder()
.model("gpt-5.2")
.input("Say this is a test")
.instructions("Talk like a pirate")
.build();
Response response = client.responses().create(params);
String generatedText = response.outputText();
System.out.println(generatedText);
In this example, the model parameter specifies the AI model, input is your prompt, and instructions provide behavioral guidance that overrides the input prompt. For production environments, always use specific model snapshots (e.g., gpt-5-2025-08-07) instead of generic names like gpt-5 to ensure consistent results. Once your request is set up, the next step is to process the API’s response effectively.
The SDK simplifies response handling by converting JSON responses into immutable classes like Response or ChatCompletion. From version 4.0.0 onwards, the SDK includes a handy method, response.outputText(), which combines all text outputs from the model into a single string. If you need more control, you can manually navigate through the object hierarchy:
response.choices().stream()
.flatMap(choice -> choice.message().content().stream())
OpenAI also recommends logging the x-request-id header included with every response. This unique identifier can help their support team troubleshoot issues if needed. You can access this identifier directly from the SDK’s response objects. For structured data extraction, you can define a custom Java class (POJO) and use the responseFormat(Class<T>) method to convert the JSON response into an instance of your class.
When dealing with errors, always check the HTTP status code and handle IOException for network-related issues. For rate-limiting, monitor the x-ratelimit-remaining-requests and x-ratelimit-reset-requests headers to implement retry logic using exponential backoff. Since all SDK classes are immutable, you can use the toBuilder() method if you need to modify any response or parameter object.
Chat Completions operate without retaining state, meaning you need to include the entire conversation history in each request. For a more streamlined approach in modern applications, the Responses API comes in handy with its previous_response_id feature, simplifying state management. For more complex, long-term interactions, the Assistants API uses server-side Threads to maintain conversation history.
"Reasoning models, like o3 and GPT-5, behave differently from chat models and respond better to different prompts. One important note is that reasoning models perform better and demonstrate higher intelligence when used with the Responses API." - OpenAI
When working with Chat Completions, maintain a List<ChatCompletionMessage> to keep track of the conversation. After every response, append both the user's input and the assistant's reply to this list before making the next API call. On the other hand, the Responses API simplifies this process. You only need to pass the previous_response_id in the ResponseCreateParams builder, which links requests seamlessly. For even more intricate workflows, the Assistants API fully automates history management.
| Feature | Chat Completions API | Responses API | Assistants API |
|---|---|---|---|
| State Management | Manual (Developer manages history) | Semi-automated (previous_response_id) |
Automated (Server-side Threads) |
| Complexity | Low | Medium | High |
| Best Use Case | Simple, short interactions | Modern text generation, reasoning models | Complex workflows, long-term state |
To manage costs effectively, monitor usage.total_tokens in API responses. Longer conversation histories increase token usage, which can add up over time. The Responses API offers a truncation parameter - setting it to auto allows the system to automatically remove older messages when the input exceeds the context window.
While text interactions are a core feature, the OpenAI API also supports advanced image generation, which is covered in the next section.
For image generation, the OpenAI Java library provides the Image API for single-prompt tasks and the Responses API for multi-turn editing. Choose the gpt-image-1.5 model for the highest quality or opt for gpt-image-1-mini if cost is a priority. Note: Support for DALL-E 2 and DALL-E 3 models will end on May 12, 2026.
To enhance user experience, implement streaming with createStreaming, which allows partial images to be displayed as they are generated. The partial_images parameter lets you receive up to three partial images during the process. Use the b64_json response format to obtain image data directly in the response, which can be decoded into bytes for immediate storage. Additionally, the revised_prompt field in the API response reveals how the model refined your input for better visual results.
When editing images with masks, ensure both the mask and the original image have identical dimensions and formats, keeping file sizes under 5MB. Before accessing GPT Image models, developers may need to complete API Organization Verification in the developer console.
Reliable API performance requires robust error handling. Keep an eye on HTTP headers like x-ratelimit-remaining-requests and x-request-id to monitor rate limits and troubleshoot issues. Use withOptions() to configure maxRetries, and for non-blocking calls, leverage .async() or OpenAIClientAsync. Pin production applications to specific model snapshots (e.g., gpt-4o-2024-08-06) to ensure consistent performance, and set truncation to disabled to identify oversized inputs.
"OpenAI recommends logging request IDs in production deployments for more efficient troubleshooting with our support team, should the need arise." - OpenAI
To track token usage, query the Usage API at /v1/organization/usage/completions. For structured outputs, use JsonSchemaLocalValidation to catch any schema violations locally before making an API call, reducing unnecessary requests and potential errors.

Building on our earlier discussion about OpenAI API integration, NanoGPT steps in as a platform offering broader model access and advanced tools.
NanoGPT allows seamless Java integration by using OpenAI-compatible endpoints alongside the official openai-java SDK. With access to over 400 AI models from providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Meta, and Google, it simplifies workflows with a single API key and unified billing system. To set it up with Java, just configure the client’s base URL to https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1.
The platform operates on a pay-as-you-go system, eliminating the need for monthly subscriptions. Users can make deposits as low as $1.00 for standard payments or $0.10 when using cryptocurrency.
For enhanced accuracy, NanoGPT offers real-time web search capabilities. By appending suffixes such as :online for standard searches or :online/linkup-deep for deeper iterative searches, factual accuracy can improve significantly - up to 10 times more accurate, according to NanoGPT’s documentation. For example, enabling web search with GPT-4o-mini enhances its factuality by 10x compared to models like o1 without web access. Pricing for these searches is straightforward: $0.006 per request for standard searches and $0.06 per request for deep searches.
Privacy is another priority for NanoGPT. It provides TEE-backed verifiable models (Trusted Execution Environment), enabling users to fetch attestation reports and signatures to ensure secure and confidential computations. Additionally, prompt caching is supported for Claude models, offering up to a 90% discount on reused tokens. For uninterrupted caching during failovers, you can set stickyProvider: true.
Here’s a quick look at how NanoGPT stacks up against the standard OpenAI API:
| Feature | NanoGPT | Standard OpenAI API |
|---|---|---|
| Model Variety | Access to 400+ models (GPT, Claude, Gemini, Llama, etc.) | Limited to OpenAI models (GPT series) |
| Pricing Model | Pay-as-you-go with a $1.00 minimum deposit | Model-specific billing or subscriptions |
| Privacy | TEE-backed verifiable models | Standard enterprise privacy terms |
| Web Access | Built-in via :online suffixes |
Requires manual tool or function calls |
| Base URL | https://nano-gpt.com/api/v1 |
https://api.openai.com/v1 |
| Prompt Caching | Supported for Claude models with ~90% token discounts | Supported for OpenAI models |
For developers looking to optimize costs in Java applications, NanoGPT provides the GET /api/v1/models?detailed=true endpoint. This allows real-time retrieval of pricing data per million tokens for every model. For instance, GPT-4o Mini is priced at $0.15 per million prompt tokens and $0.60 per million completion tokens, while Claude 3.5 Sonnet costs $3.00 per million prompt tokens and $15.00 per million completion tokens. This flexible billing aligns well with previously discussed cost-saving strategies.
Keeping production Java applications cost-efficient begins with smart client management. As mentioned earlier, reusing a single shared client instance can significantly improve efficiency.
Choosing the right model for your tasks can also make a big difference in managing costs. For complex tasks, gpt-5 might be ideal, but for simpler operations, consider using gpt-5-mini or gpt-5-nano to minimize token usage and reduce latency.
"One useful framework for thinking about reducing costs is to consider costs as a function of the number of tokens and the cost per token".
To keep token usage low, focus on writing concise prompts, setting lower max_tokens parameters, and using stop sequences to avoid unnecessary output generation.
Caching is another effective way to reduce API calls. Tools like Redis or filesystem caching can help store frequent responses. For a smoother user experience, use the createStreaming method to receive response chunks as they’re generated, which reduces the time to display the first token. Additionally, the .async() method allows for non-blocking calls through CompletableFuture, keeping your application responsive even under heavy load.
To avoid unexpected expenses, set up billing alerts on the OpenAI usage limits page. These alerts can notify you via email when spending exceeds specific thresholds. It's also a good idea to separate staging and production environments, applying custom rate and spending limits for each. Keep an eye on rate limits by checking HTTP response headers like x-ratelimit-remaining-tokens and x-ratelimit-remaining-requests. Monitoring these can help you adjust request frequency dynamically and avoid hitting 429 errors.
While cost management is crucial, protecting your credentials and data is just as important.
In addition to optimizing usage, implementing strong security measures is a must. Avoid hard-coding API keys in your source code or committing them to repositories. Instead, use OpenAIOkHttpClient.fromEnv() to load keys from environment variables, or leverage secret management tools like AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, or Azure Key Vault for production environments.
Set access controls in your project settings to limit exposure. Assign "Reader" roles to team members who only need to make API requests, while reserving "Owner" roles for those managing billing and team access. This reduces the risk of internal misuse. For debugging in production, always log the x-request-id from API response headers for better traceability (refer to "Handling API Responses" for more details).
To safeguard user data, implement data privacy practices such as encrypting data in transit and anonymizing sensitive information before sending it to the API. Use secure coding techniques like input sanitization to prevent prompt injection attacks and ensure error handling doesn’t expose system details. When working with Structured Outputs, redact sensitive JSON data from error logs, as conversion errors may inadvertently reveal raw response content.
By following these best practices, your Java integration can remain efficient, secure, and scalable. For consistent behavior across updates, use pinned model versions instead of generic names. Keep staging and production environments separate to avoid disruptions during development. Be cautious when using Beta-prefixed classes in the Java SDK, as these experimental features may change over time.
Start with the basics - core authentication and request patterns - then gradually introduce advanced features like streaming, caching, and asynchronous calls while keeping a close eye on usage and security. With proper client management, thoughtful model selection, and strong security measures, you'll be set up for long-term success with your Java integration.
To keep your OpenAI API key safe in a Java application, steer clear of hardcoding it in your source code or including it in version control. A better approach is to store the key in an environment variable or a configuration file that’s excluded from your repository. When your application runs, you can retrieve the key using System.getenv() or load it from a secure properties file.
Make sure to limit the API key's permissions to only what’s absolutely necessary, and always handle API calls through your server-side code. For extra security in a production environment, you might want to use a secret management tool like AWS Secrets Manager or HashiCorp Vault. Additionally, it’s a good practice to rotate your API key regularly and keep an eye on usage patterns to detect any suspicious activity.
The Responses API and the Chat Completions API both focus on generating text, but they cater to different needs. The Responses API is ideal for straightforward tasks where you input a prompt and receive a single, direct output.
In contrast, the Chat Completions API is built for conversational AI. It enables more interactive exchanges, mimicking a natural back-and-forth dialogue. This makes it a great fit for projects like chatbots or applications requiring multi-turn conversations.
Each API shines in its own way, so the choice between them depends on what your project demands. For simple text generation, go with the Responses API. For dynamic, conversational interactions, the Chat Completions API is the way to go.
To keep expenses in check and make the most of your tokens, focus on crafting concise prompts and setting a low max_tokens value. Whenever possible, reuse cached inputs to avoid unnecessary processing. For simpler tasks, consider using more affordable models like GPT-5 Mini. If you're handling large-scale operations, the Batch API can be a game-changer for cutting costs. Also, make it a habit to track your usage through the platform's dashboard or the usage field in API responses to maintain control over your spending.